Description:
Explore the fundamentals of What is CAD 3D Modeling in this beginner-friendly guide. Learn what CAD 3D modeling is, how it works, where it’s used, and why it’s essential in engineering, architecture, manufacturing, and design.
Introduction
In the world of modern design, CAD 3D modeling stands as one of the most revolutionary technologies. Whether you’re designing a car engine, a high-rise building, or a smartphone casing, CAD (Computer-Aided Design) 3D modeling plays a crucial role in turning imagination into reality. From engineers and architects to product designers and animators, professionals across many industries rely on CAD 3D modeling for precision, innovation, and efficiency.
But what exactly is What is CAD 3D Modeling? How does it work, and why has it become such a critical part of design and manufacturing processes? This blog breaks down everything you need to know.
What is CAD 3D Modeling?
CAD 3D modeling is the process of creating three-dimensional digital representations of physical objects using computer software. Unlike 2D drafting, which involves flat drawings, What is CAD 3D Modeling allows designers to visualize and manipulate their designs in a fully spatial environment.
The model can be rotated, zoomed in or out, and inspected from all angles. It provides depth, scale, and realistic dimensions, allowing users to create virtual prototypes that can be analyzed, tested, or directly used for manufacturing.
Key Features What is CAD 3D Modeling
CAD 3D modeling software offers tools and features to simplify complex design processes. Here are the essential features:
- Solid Modeling: Defines the volume and shape of a 3D object. Solid models are often used in mechanical engineering and manufacturing.
- Surface Modeling: Deals with the exterior shape of objects, ideal for aesthetic and aerodynamic designs.
- Parametric Design: Allows designers to control features and dimensions using mathematical equations and relationships.
- Assemblies: Enables multiple parts to be joined into one system to simulate how they interact.
- Simulation & Testing: Some CAD software includes analysis tools for stress, heat, or motion simulation.
Popular What is CAD 3D Modeling
Many powerful tools are available for CAD 3D modeling. Some of the most widely used include:
- AutoCAD 3D – A general-purpose CAD tool by Autodesk.
- SolidWorks – Popular in mechanical engineering and product design.
- Fusion 360 – Combines CAD, CAM, and CAE tools in one platform.
- CATIA – Used for aerospace, automotive, and advanced manufacturing.
- PTC Creo – A powerful parametric design software.
- SketchUp – Ideal for architectural modeling and simple designs.
- Blender – Though primarily for animation and art, it’s useful in design prototyping.
What is CAD 3D Modeling Works
- Sketching the Base Profile
Most CAD 3D models begin with a 2D sketch—a simple shape like a rectangle, circle, or polygon that serves as the base. - Extrusion and Revolve
Using tools like extrude, revolve, or loft, the 2D shape is given depth and volume to create a 3D object. - Feature Building
Further features such as holes, chamfers, and fillets are added. Boolean operations allow combining or subtracting shapes. - Assemblies and Constraints
Multiple parts can be assembled with real-world relationships like joints, hinges, and fasteners. - Simulation (Optional)
Some models are tested using simulations for load-bearing, thermal behavior, or motion constraints. - Rendering and Export
The final design can be rendered with textures and lighting or exported as STL/OBJ files for 3D printing or CNC machining.
Applications What is CAD 3D Modeling
CAD 3D modeling is used in countless fields. Below are some major industries where it plays a vital role:
1. Mechanical Engineering
- Design of machines, tools, and automotive parts.
- 3D simulation of moving assemblies.
- Rapid prototyping for product development.
2. Architecture and Construction
- Visualization of building structures.
- Creation of floor plans, elevation models, and landscape layouts.
- BIM (Building Information Modeling) integration.
3. Product Design
- Prototypes of gadgets, furniture, packaging, etc.
- Ergonomic testing and material simulation.
- Design for injection molding and mass production.
4. Aerospace and Automotive
- Design of engine components, wings, turbines.
- Performance testing under pressure and heat.
- Aerodynamic surface modeling.
5. Medical and Biotech
- Creation of prosthetics and implants.
- Custom surgical tools and devices.
- Anatomical modeling for educational purposes.
6. Entertainment and Animation
- Characters, environments, and props.
- Game design and cinematic special effects.
Benefits of CAD 3D Modeling
Why is CAD 3D modeling such a big deal? Here’s what makes it indispensable:
- Precision: CAD allows for exact measurements and dimensions.
- Visualization: See your design in realistic 3D before it’s built.
- Time Efficiency: Changes and iterations are faster compared to hand-drawing.
- Collaboration: Models can be shared digitally for feedback and teamwork.
- Simulation: Test performance before manufacturing, reducing risk.
- Cost Savings: Fewer physical prototypes are needed.
- Documentation: Automatically generate drawings, BOMs, and specs.
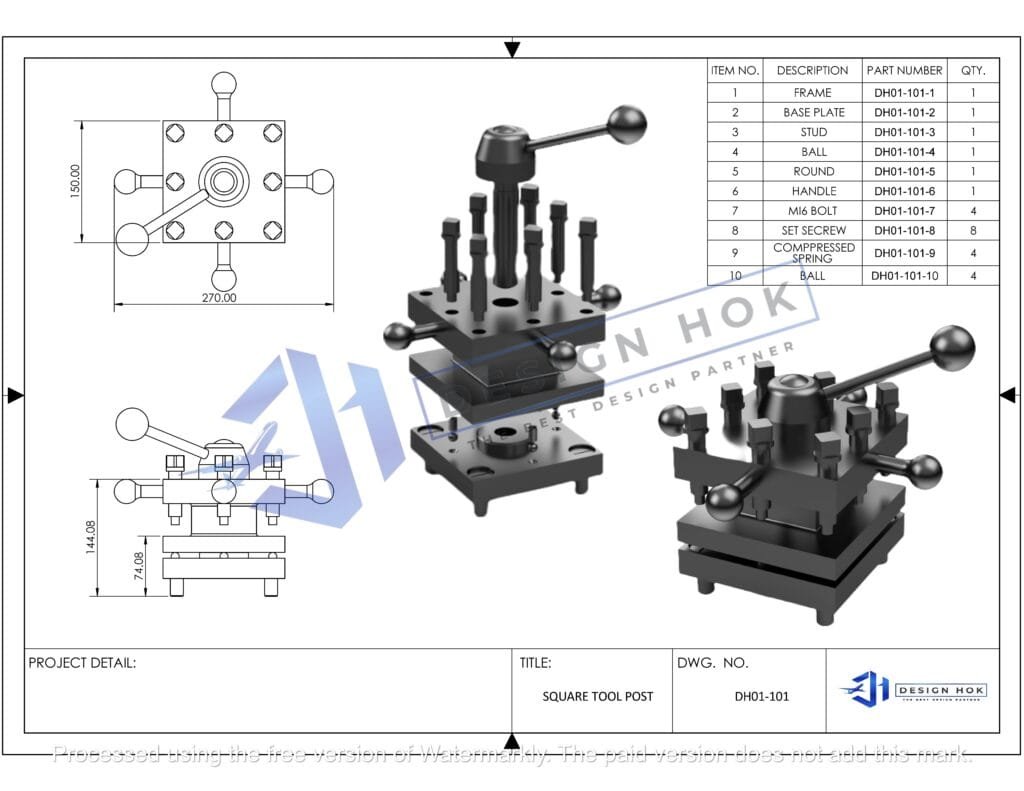
CAD 3D Modeling in the Design Process
CAD 3D modeling often fits into a broader product development cycle, such as:
- Conceptualization
Ideas are turned into basic sketches and rough 3D shapes. - Design and Development
Detailed 3D models are created with specifications, materials, and assemblies. - Testing and Analysis
The model is tested under real-world conditions using simulation tools. - Prototyping
Models are exported to 3D printers or CNC machines for real-world testing. - Manufacturing
The final design is used to produce molds, components, or assemblies at scale. - Marketing and Presentation
Rendered 3D models are used for promotional materials or product showcases.
Future of CAD 3D Modeling
With the growth of AI, cloud computing, and VR/AR, What is CAD 3D Modeling is advancing rapidly. Real-time collaboration, AI-assisted design, and immersive virtual modeling are becoming the norm.
Tools like cloud-based CAD (e.g., Fusion 360) allow global teams to work together, while AI-driven optimizations suggest the best material usage or structural strength. As manufacturing embraces Industry 4.0, CAD will only become more integrated with smart machines, robotics, and digital twins.
Conclusion
What is CAD 3D Modeling is much more than a design tool—it’s a digital foundation for innovation. From sketch to simulation, it brings clarity, control, and creativity to the product development process. Whether you’re designing a new smartphone case, a robotic arm, or a skyscraper, CAD 3D modeling helps you turn ideas into reality with speed, accuracy, and confidence.
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of What is CAD 3D Modeling, empowering designers, engineers, and creators to build a smarter and more efficient world.
FAQs: What is CAD 3D Modeling?
Q1: What does CAD stand for?
CAD stands for Computer-Aided Design, a digital tool used to create, edit, and analyze designs.
Q2: What is the difference between 2D drafting and 3D modeling?
2D drafting involves flat drawings (like floor plans), while 3D modeling creates objects with height, depth, and perspective.
Q3: Is CAD 3D modeling used in 3D printing?
Yes. CAD models can be exported as STL files and used directly in 3D printers for prototyping or production.
Q4: What skills do I need to learn CAD 3D modeling?
Basic computer knowledge, understanding of geometry, and familiarity with design software. Engineering or design background is helpful but not necessary for beginners.
Q5: Is CAD 3D modeling difficult to learn?
It depends on the software and complexity of the designs. With practice and tutorials, even beginners can become proficient.
Q6: Can I use CAD software for free?
Yes, several free tools like FreeCAD, TinkerCAD, and SketchUp (Free version) are available for beginners and hobbyists.
Q7: What is the best CAD software for beginners?
Fusion 360, TinkerCAD, and SketchUp are user-friendly for beginners. SolidWorks and AutoCAD are more advanced.





