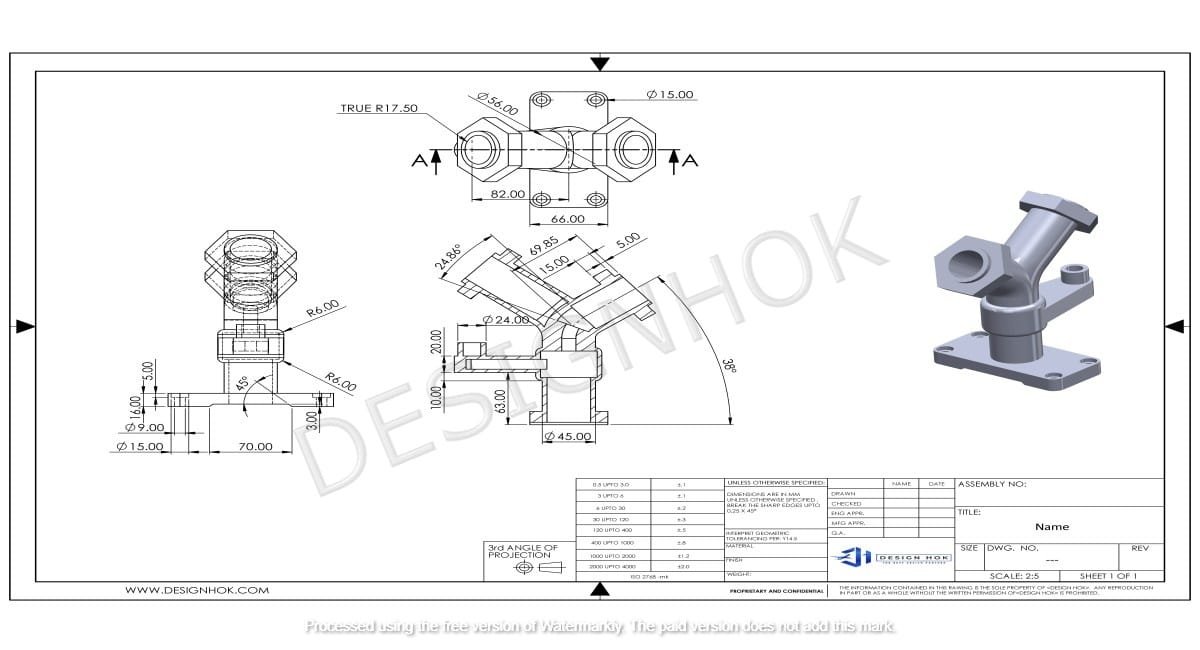
Why Engineers Still Create 2D Detailed Drawings remain a staple in engineering design. the reasons why engineers continue to rely on 2D drawings for critical aspects of product design and manufacturing. From their role in precision documentation to their ease of use on the shop floor, 2D drawings provide valuable clarity in the design process.
Introduction Why Engineers Still Create 2D Detailed Drawings
fast-paced technological world, 3D modeling and computer-aided design (CAD) software have revolutionized the field of engineering. With the ability to create highly detailed, realistic visualizations, one might wonder why engineers still rely on 2D detailed drawings. After all, with the advent of virtual reality (VR) and digital twins, 3D models seem to offer superior insights into design and assembly. However, the reality is that 2D drawings remain an essential tool in the engineering industry for many reasons. These simple yet highly detailed visualizations play a critical role in the design and manufacturing process. In this article, we’ll explore the key reasons why 2D detailed drawings continue to be indispensable to engineers.
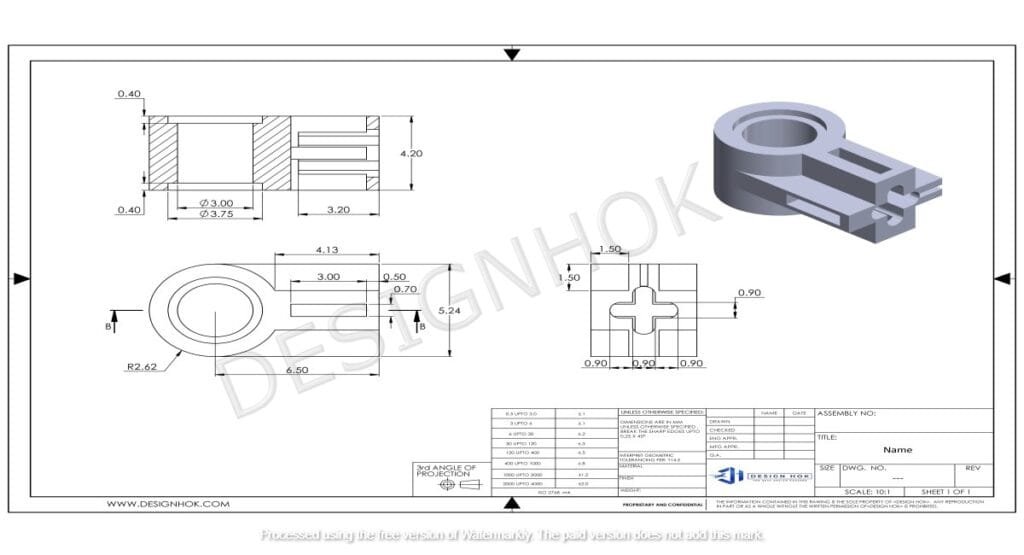
Clear and Concise Communication
One of the primary reasons engineers still create 2D detailed drawings is their ability to communicate design information clearly and concisely. While 3D models provide a comprehensive view of a product, they can sometimes overwhelm with excessive detail or complexity. On the other hand, 2D drawings break down the design into specific views, such as top, front, and side, which helps simplify communication among team members. These orthographic projections offer a straightforward way to represent dimensions, materials, and tolerances, ensuring that everyone involved in the process—from designers to machinists—understands the exact specifications of a part.
Moreover, Why Engineers Still Create 2D Detailed Drawings allow for easy annotation. Engineers can include critical notes, such as material specifications, finish requirements, or machining instructions, directly on the drawing. These annotations are usually standardized, allowing anyone familiar with engineering drawings to interpret the information quickly and accurately.
Precision in Dimensional Accuracy Why Engineers Still Create 2D Detailed Drawings
Why Engineers Still Create 2D Detailed Drawings are excellent for visualizing a product’s overall shape and functionality, they are often less precise when it comes to documenting exact dimensions. Why Engineers Still Create 2D Detailed Drawings excel in providing exact measurements and tolerances, making them vital for manufacturing. These drawings provide a flat, two-dimensional representation of every part, which enables engineers to specify exact lengths, widths, depths, and angles with extreme accuracy. This precision is critical in industries where even a tiny deviation in measurement can result in a product failure or safety risk.
Manufacturing facilities, especially those that rely on manual processes or less sophisticated machinery, often depend on 2D drawings for fabricating components. While 3D models might offer a high-level view, machinists and operators can refer to the 2D drawings to follow the exact dimensions and ensure the final product meets all specifications.
Compatibility with Traditional Processes Why Engineers Still Create 2D Detailed Drawings
Despite the rise of digital technologies, many traditional engineering and manufacturing processes still rely on 2D drawings. For instance, in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction, 2D drawings have long been the standard for communicating designs. These industries often operate under strict regulatory guidelines that require detailed documentation in a 2D format.
In many cases, these regulatory bodies and certification organizations still require physical copies of Why Engineers Still Create 2D Detailed Drawings as part of their approval processes. Engineers use these drawings to ensure compliance with industry standards, making it essential to maintain 2D documentation alongside more modern 3D models. Additionally, fabrication shops, particularly those that have been in operation for decades, often have workflows built around 2D drawings. While some shops have adopted 3D modeling tools, many still rely on 2D prints as their primary source of information.
Cost Efficiency and Speed
Creating and reviewing Why Engineers Still Create Why Engineers Still Create 2D Detailed Drawings can be more cost-effective and faster than producing complex 3D models. While 3D models are highly detailed and often necessary for certain types of analysis or simulations, they require more time and computational resources to create and manipulate. 2D drawings, by contrast, are simpler to produce and can be generated quickly, especially for smaller projects that do not require extensive design validation.
For projects where time and budget constraints are a concern, 2D drawings offer a practical solution. They can be easily reviewed and approved by team members and clients without the need for specialized software or extensive training. This simplicity is particularly valuable in industries where rapid prototyping and iterative design changes are common.
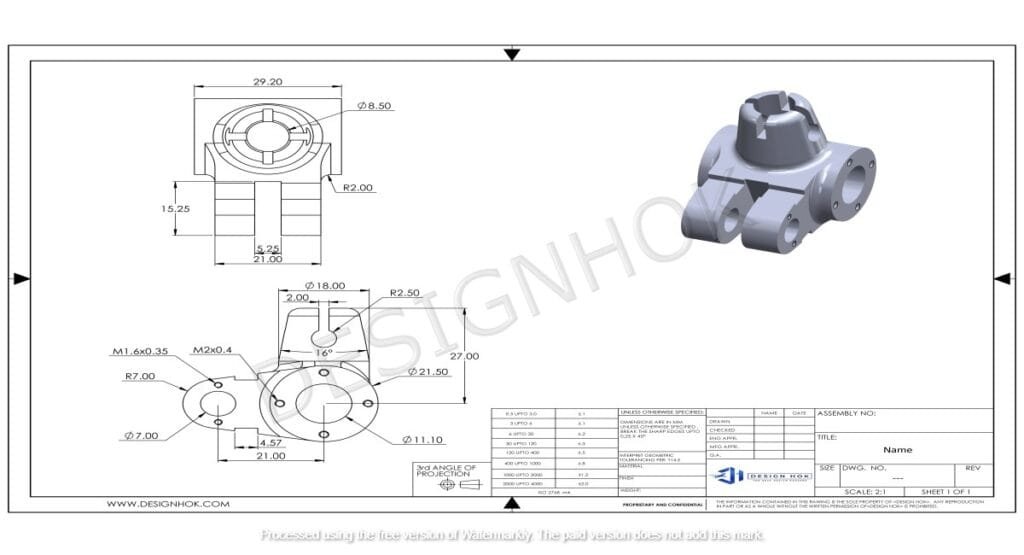
Industry Standardization
The use of Why Engineers Still Create 2D Detailed Drawings remains deeply ingrained in engineering standards and practices. Industry standards organizations, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) and ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers), still base many of their guidelines on 2D drawing conventions. These standards ensure consistency and reliability across engineering practices, making it easier for companies to collaborate and for products to be manufactured to exact specifications.
Engineers often rely on these standardized 2D drawings for cross-functional teams and suppliers, especially in global operations. By following standardized drawing practices, companies can ensure that their designs are understood and produced accurately, regardless of where the manufacturing takes place.
Conclusion
While Why Engineers Still Create 2D Detailed Drawings and advanced digital tools have transformed engineering design, 2D detailed drawings continue to play a vital role in the industry. Their ability to clearly communicate design intent, document precise measurements, and align with traditional processes makes them an indispensable tool. Engineers rely on 2D drawings for their simplicity, speed, and compatibility with existing workflows, ensuring that these drawings remain relevant even in an age of rapidly advancing technology.
FAQs
1. Why do engineers still use 2D drawings when 3D modeling is available?
While 3D modeling provides a comprehensive view, 2D drawings are often more precise, easier to communicate, and faster to produce. They simplify the documentation of exact dimensions and tolerances, making them essential for manufacturing and compliance.
2. Are 2D drawings outdated in modern engineering?
No, 2D drawings are not outdated. They remain essential in many industries due to their ability to provide clear, standardized documentation that is compatible with both traditional and modern manufacturing processes.
3. What are the advantages of 2D drawings over 3D models?
2D drawings offer precision in documenting exact dimensions, are faster to create and review, and are compatible with regulatory standards and traditional manufacturing workflows.
4. Do all engineers need to know how to create 2D drawings?
Yes, most engineers still need to know how to create and interpret 2D drawings, as they are a key part of many industries’ design and manufacturing processes.