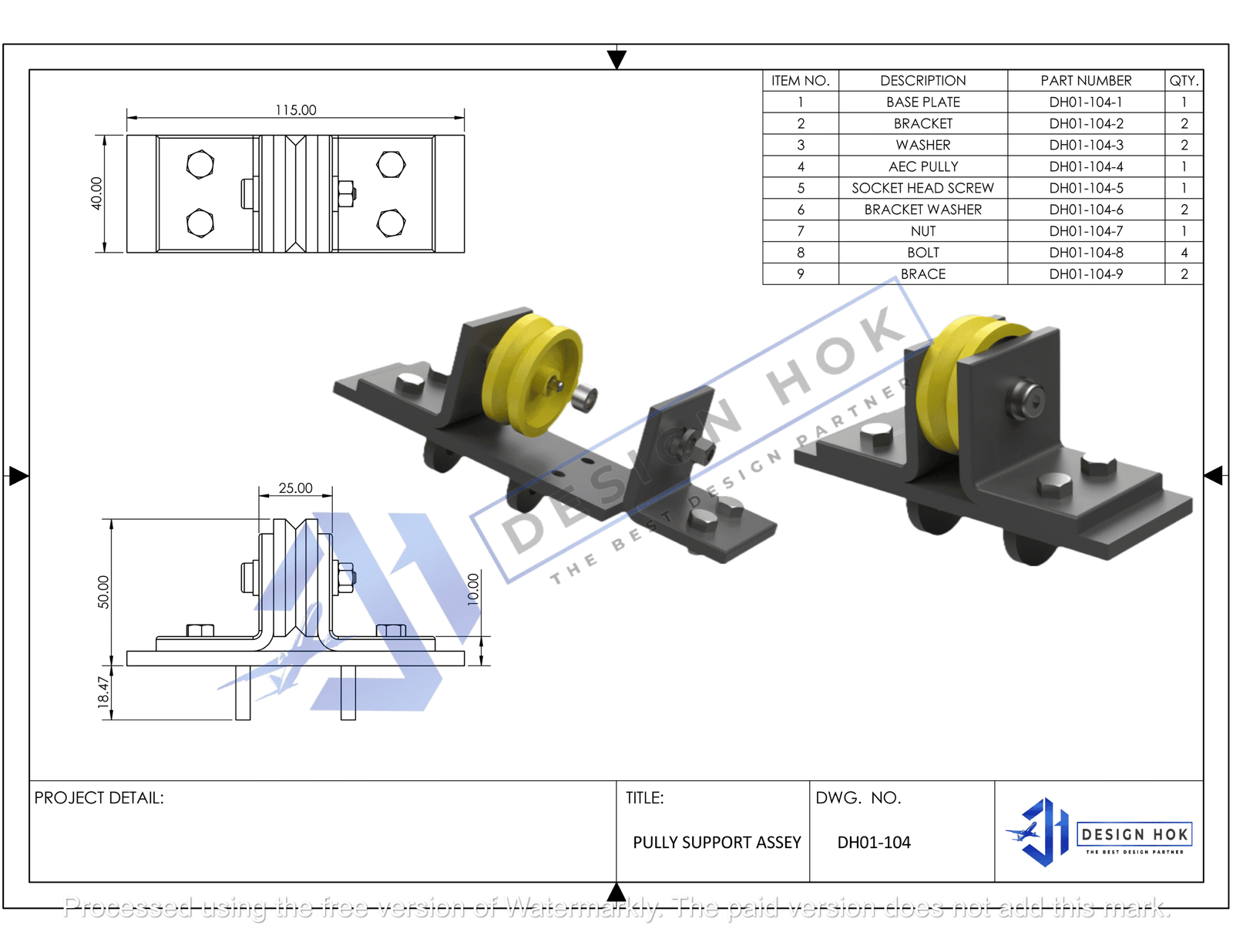
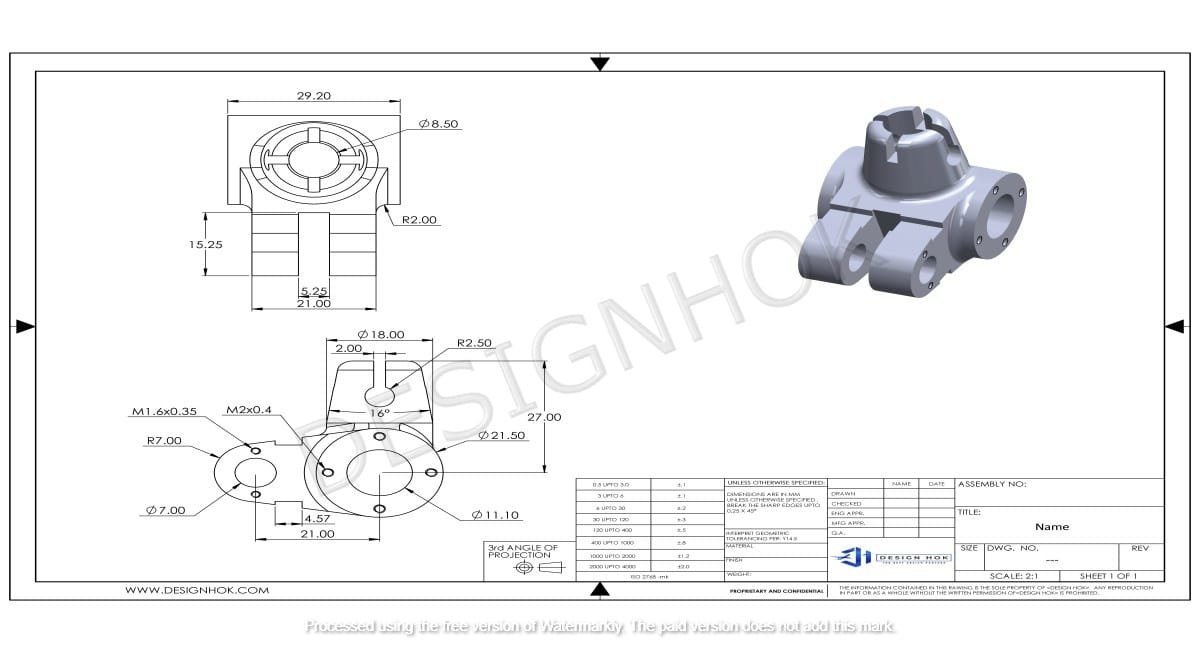
Introduction
What is Rendering in 3D Modeling that transforms a raw 3D model into a high-quality visual representation. It involves processing a model with lighting, textures, and effects to create realistic or stylized images. Whether you’re designing architectural structures, mechanical components, or animated scenes, rendering helps bring your vision to life with stunning detail.
For DesignHok, a company specializing in mechanical design, What is Rendering in 3D Modeling, and rendering, mastering rendering techniques is crucial for creating high-quality visuals that showcase design concepts effectively. This blog will explore what rendering is, its types, processes, and how it benefits 3D modeling.
What is Rendering in 3D Modeling?
Rendering is the process of generating a 2D image or animation from a 3D model using specialized software. It involves adding lighting, textures, shadows, reflections, and other elements to enhance the appearance of a model. The goal is to create an image that looks as realistic or artistic as possible.
Rendering is widely used in industries like architecture, product design, film, gaming, and mechanical engineering. It allows designers and clients to visualize a final product before physical production begins, making it an invaluable tool for decision-making and presentation.
Types of Rendering in 3D Modeling
What is Rendering in 3D Modeling can be categorized into different types based on the technique and purpose. The two main types are real-time rendering and pre-rendered (offline) rendering.
1. Real-Time Rendering
Real-time rendering is used in video games, simulations, and interactive applications. It processes images at high speeds to provide immediate feedback. This type of rendering is optimized for fast performance and is commonly seen in gaming engines like Unity and Unreal Engine.
Characteristics of Real-Time Rendering:
- Instant feedback with minimal delay
- Lower resolution compared to pre-rendered images
- Requires powerful hardware for smooth performance
- Used in gaming, virtual reality (VR), and interactive design
2. Pre-Rendered (Offline) Rendering
Pre-rendered What is Rendering in 3D Modeling is used for high-quality images and animations that don’t need real-time updates. It takes more time to process but results in superior visual quality, making it ideal for architecture, mechanical design, and animated movies.
Characteristics of Pre-Rendered Rendering:
- Higher quality with realistic lighting and details
- Takes longer to process (minutes to hours per frame)
- Used in architecture, product design, animation, and mechanical engineering
- Requires high-performance computers for rendering complex scenes

The Rendering Process in 3D Modeling
The rendering process consists of multiple steps, from setting up a scene to final output. Here’s how rendering is done in 3D modeling:
1. Creating the 3D Model
Before What is Rendering in 3D Modeling must be designed using software like Autodesk 3ds Max, Blender, Maya, or SolidWorks. The model acts as the base structure for rendering.
2. Applying Materials and Textures
Materials define how the surface of a 3D model looks. Textures add details like wood grain, metal reflections, or fabric patterns to enhance realism. PBR (Physically Based Rendering) materials help achieve accurate lighting and reflections.
3. Setting Up Lighting
Lighting plays a crucial role in rendering. Different types of lighting setups can be used, such as:
- Ambient lighting – softens shadows and brightens scenes
- Point lights – emit light in all directions, like a bulb
- Directional lights – simulate sunlight and cast long shadows
- Spotlights – focus light on specific areas
4. Adjusting Camera Angles
Just like in photography, positioning the camera in the right angle enhances composition. Depth of field, focal length, and perspective are adjusted to create visually appealing shots.
5. Rendering Settings
Rendering settings control the quality and speed of the process. Common settings include:
- Resolution – determines image clarity (e.g., 1080p, 4K)
- Anti-aliasing – smooths jagged edges in the image
- Ray tracing – improves reflections and shadows for realism
- Sampling rate – affects the accuracy of light calculations
6. Rendering the Final Image or Animation
Once all settings are configured, the rendering software processes the scene and generates the final image or animation. Depending on the complexity, rendering can take from a few seconds to several hours.
7. Post-Processing and Editing
After rendering, post-processing is done using software like Adobe Photoshop or After Effects. This includes color correction, adding effects, and enhancing details for a more polished look.

Benefits of What is Rendering in 3D Modeling
Rendering is essential for industries that rely on What is Rendering in 3D Modeling. Here are some key benefits:
1. Realistic Visualization
Rendering creates photorealistic images that help designers and clients visualize products, buildings, and mechanical components before production.
2. Improved Decision-Making
Rendered models provide a clear picture of how a final product will look, allowing stakeholders to make informed decisions and modifications before investing in manufacturing.
3. Enhanced Marketing and Presentation
High-quality rendered images are used in marketing materials, advertisements, and presentations to attract customers and investors.
4. Cost and Time Savings
Rendering helps identify design flaws before manufacturing, reducing costly mistakes and saving time in product development.
5. Better Communication
Rendered visuals help designers, engineers, and clients communicate complex ideas more effectively than traditional sketches or blueprints.
Rendering Software for 3D Modeling
There are several rendering software options available, each suited for different needs:
- V-Ray – Known for high-quality architectural and product rendering
- Blender Cycles & Eevee – Free and versatile rendering engines
- Autodesk Arnold – Used in film production and high-end visual effects
- KeyShot – Great for product visualization and mechanical design
- Lumion – Popular for architectural rendering
Conclusion
Rendering is a vital step in 3D Modeling that enhances the visual quality of models by adding realistic lighting, textures, and effects. It plays a crucial role in architecture, engineering, animation, and product design, making it an indispensable tool for professionals.
For companies like DesignHok, rendering helps create high-quality visual presentations for clients, improves decision-making, and enhances marketing efforts. Whether you’re working with real-time rendering for interactive applications or pre-rendered images for high-end visualization, mastering rendering techniques can elevate your 3D modeling projects to the next level.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is rendering in 3D modeling?
Rendering is the process of generating high-quality images or animations from 3D models by adding lighting, textures, and effects.
2. What are the types of rendering?
The two main types of rendering are real-time rendering (used in gaming and VR) and pre-rendered rendering (used in architecture, animation, and engineering).
3. Which software is best for 3D rendering?
Popular rendering software includes V-Ray, Blender Cycles, Autodesk Arnold, KeyShot, and Lumion. The choice depends on your industry and requirements.
4. How long does rendering take?
Rendering time varies based on complexity. Simple images may take seconds, while high-resolution animations can take hours or even days.
5. Why is rendering important in 3D modeling?
Rendering helps visualize designs realistically, improves decision-making, enhances presentations, and saves costs by identifying design flaws early.