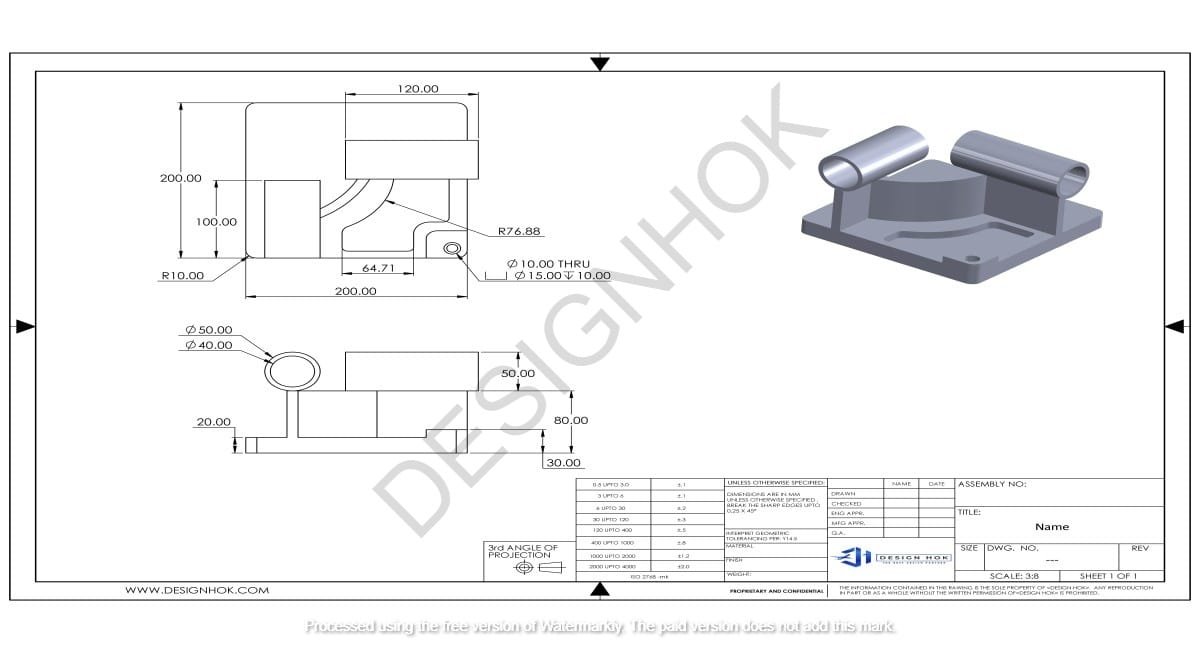
Description:
What Are the Different 3D Modeling Methods plays a vital role in design, engineering, animation, and product development. This guide explores the different What Are the Different 3D Modeling Methods—such as solid, surface, wireframe, sculpting, and parametric modeling—explaining their uses, benefits, and when to apply each method.
Introduction
In the world of digital design and engineering, What Are the Different 3D Modeling Methods is more than just shaping virtual objects—it’s a tool that transforms ideas into reality. Whether you’re developing a product prototype, crafting an architectural space, or animating a game character, the method you choose for What Are the Different 3D Modeling Methods makes a huge difference in the final outcome.
There are various What Are the Different 3D Modeling Methods, each designed to serve different purposes based on project goals, industry needs, and technical requirements. Understanding these techniques helps designers and engineers select the right approach for their work and create models that are accurate, realistic, and functional.
This blog will walk you through the different types of What Are the Different 3D Modeling Methods, explaining their core principles, applications, and advantages, with examples from industries like product design, architecture, animation, and mechanical engineering.
1. Solid Modeling
What It Is:
Solid modeling is one of the most precise and engineering-focused types of What Are the Different 3D Modeling Methods. It represents objects with complete volume, mass, and density. These models are typically created using parametric CAD software like SolidWorks, Fusion 360, or AutoCAD.
Key Features:
- Fully enclosed, solid volumes
- Accurate dimensions and constraints
- Boolean operations (union, subtract, intersect)
Best For:
- Mechanical parts
- Engineering designs
- Product prototyping
- Manufacturing-ready models
Advantages:
- Highly accurate and measurable
- Great for simulations and stress analysis
- Ideal for 3D printing and CNC machining
Example:
Designing a gearbox assembly for an industrial machine using precise hole placements and load-bearing calculations.
2. Surface Modeling
What It Is:
Surface modeling deals with the outer “skin” of an object. It creates complex, smooth, and flowing surfaces without defining internal volume. This method is often used when appearance is more important than mass.
Key Features:
- Manipulation of curves and control points
- Flexible and smooth design of surfaces
- Does not define internal material properties
Best For:
- Automotive design
- Aircraft body design
- Consumer product casings
- Industrial design concepts
Advantages:
- Highly flexible for organic shapes
- Useful for styling and aesthetic modeling
- Allows intricate surface control
Example:
Creating the aerodynamic body of a concept car with smooth curves and precise surface transitions.
3. Wireframe Modeling
What It Is:
Wireframe modeling is one of the earliest and most basic What Are the Different 3D Modeling Methods techniques. It defines shapes using lines and vertices without surfaces or volume. While rarely used alone in modern workflows, it forms the foundation for other modeling types.
Key Features:
- Only edges and vertices are visible
- Offers a skeleton-like structure
- No surface detail or rendering support
Best For:
- Conceptual modeling
- Early design drafts
- Technical visualization
Advantages:
- Lightweight file size
- Fast editing and computation
- Easy to visualize structural layout
Example:
Outlining the internal frame of a building or a machine part before adding details and surfaces.
4. Polygonal Modeling (Mesh Modeling)
What It Is:
Polygonal modeling is the most commonly used method in media, gaming, and visual effects. It represents 3D objects using flat surfaces (polygons), usually quads or triangles. Software like Blender, Maya, and 3ds Max are commonly used for this.
Key Features:
- Uses vertices, edges, and faces
- Editable mesh topology
- Supports UV mapping and texturing
Best For:
- Animation
- Game development
- Character modeling
- Visual effects
Advantages:
- Good balance between control and realism
- Easily animated and textured
- Highly flexible for detailed models
Example:
Modeling a video game character with facial features, armor, and accessories for animation.
5. Sculpting (Digital Sculpting)
What It Is:
Digital sculpting is an artistic approach to modeling. It mimics real-world clay sculpting by allowing users to push, pull, smooth, and pinch geometry with brushes. This method is ideal for creating high-detail organic shapes.
Key Features:
- Uses a high-resolution mesh
- Brush-based tools for shaping
- Often combined with normal/displacement maps
Best For:
- Character modeling
- Creature design
- Artistic concept models
Advantages:
- Extreme detail and realism
- Natural, intuitive modeling
- Perfect for organic shapes
Example:
Creating a fantasy dragon with scales, muscles, and fine textures using ZBrush or Blender’s sculpt mode.
6. Parametric Modeling
What It Is:
Parametric modeling uses defined parameters (length, width, height, angles) and relationships (constraints) to create intelligent models. Changes in one part automatically update related parts.
Key Features:
- Driven by dimensions and constraints
- Feature-based design tree
- Design history is maintained
Best For:
- Engineering and product design
- Repetitive or standardized parts
- Precision-driven industries
Advantages:
- Easily editable and updateable
- Maintains design intent
- Perfect for iterative design
Example:
Designing a mechanical bracket with slots that automatically adjust size when the main body dimensions change.
7. NURBS Modeling (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines)
What It Is:
NURBS modeling uses mathematical curves to generate smooth and precise geometry. This method is particularly useful when high-quality surfaces are required.
Key Features:
- Uses control points to define curves
- Smooth and continuous surfaces
- Ideal for high-precision models
Best For:
- Automotive and aerospace design
- High-quality surface modeling
- Jewelry and product styling
Advantages:
- Extremely accurate
- Great for curved surfaces
- Compatible with CAD and CAM workflows
Example:
Creating the sleek, curved outer casing of a smartwatch or an airplane wing surface.
Conclusion
Each What Are the Different 3D Modeling Methods has its strengths and specific applications. While some methods like solid and parametric modeling are favored in engineering for their accuracy and control, others like polygonal or sculpting shine in creative industries for their flexibility and realism.
Choosing the right 3D modeling method depends on:
- The nature of your project
- The level of detail required
- The end use (e.g., animation, manufacturing, presentation)
- The software tools you’re comfortable using
At DesignHok, we use a blend of these What Are the Different 3D Modeling Methods to deliver high-quality, purpose-driven designs. Whether it’s engineering parts, product mockups, or detailed visual presentations, we adapt our modeling approach to meet project goals efficiently and effectively.
FAQs: What Are the Different 3D Modeling Methods?
Q1: Which 3D modeling method is best for mechanical design?
Solid modeling and parametric modeling are best for mechanical design due to their precision and feature-based control.
Q2: Can I use multiple modeling methods in one project?
Yes! Many professionals combine techniques. For example, use solid modeling for the structure and sculpting for detailed textures.
Q3: What’s the difference between surface and solid modeling?
Solid modeling defines volume and mass; surface modeling defines only the outer surface. Solid modeling is more accurate for engineering, while surface modeling is better for aesthetics.
Q4: Which software is good for polygonal modeling?
Popular tools include Blender, Autodesk Maya, and 3ds Max for polygonal modeling in games and animation.
Q5: Is sculpting used in engineering design?
Not typically. Sculpting is more suited to artistic and organic shapes rather than precise, measurable objects required in engineering.
Q6: What is wireframe modeling used for today?
Wireframe is mostly used during the early concept stages or for quick structural overviews. It’s rarely used for final models.
Q7: Can I 3D print models made with all these methods?
Most models can be converted to formats like .STL or .OBJ for 3D printing, but they often need to be “watertight” and properly optimized.