Introduction
Mechanical threads are used in a number of areas. They are used in screws, bolts, pipe fittings, and gear shafts. They are tiny parts that help hold pieces together. You can also move things or transfer forces. However, there are various types of mechanical threads with different shapes or strengths. Let us talk about mechanical threads in full detail. We will talk about types, names, applications, and others.
1. Types of Mechanical Threads Explained
Types of mechanical threads are spiral grooves cut on a conical shape. These mechanical threads help screws, bolts, and other fasteners fit firmly. It also allows them to hold together.
Threads can be found both on the inside and outside surfaces of a part.
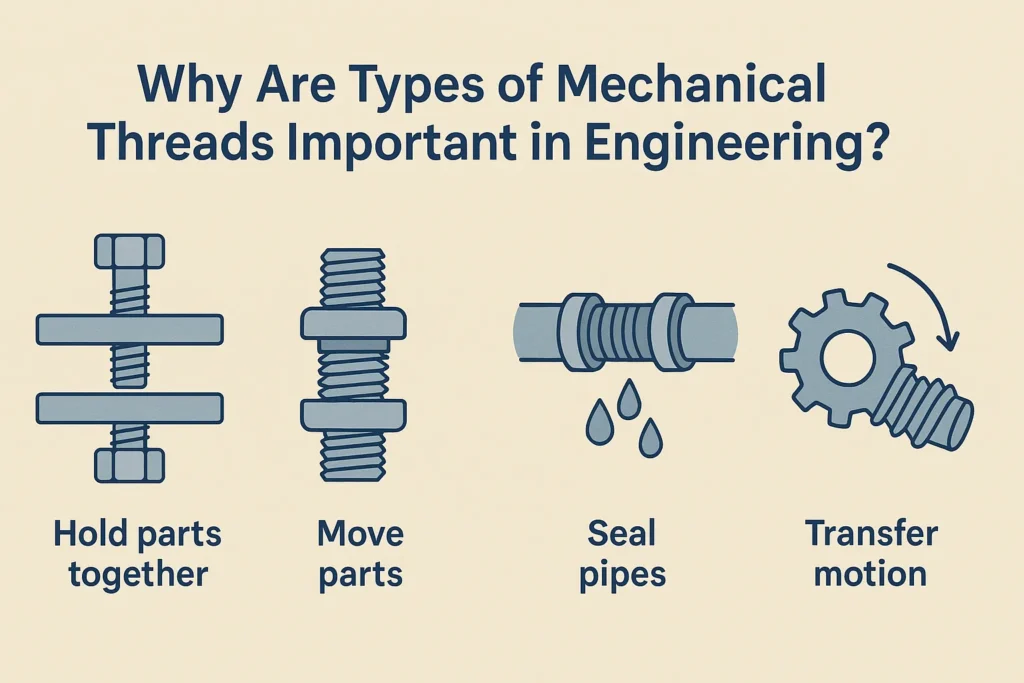
2. Importance of the Types of Mechanical Threads
Different types of Mechanical Threads are used to:
- Hold parts together securely (fastening)
- Move parts (such as in jackscrews or lead screws)
- Seal pipes and prevent leaks
- Transfer motion in machines
You can find them in various industries. These include automotive, aerospace, etc.
3. Method to Create Different Types of Mechanical Threads
Various types of Mechanical Threads that can be made using:
- Cutting tools
- Compressing the metal by rolling
- Grinding it
- Casting or molding
This method can work best if you know the material, accuracy, and production scale.
4. Main Types of Mechanical Threads
Mechanical threads are divided into two major types:
External Threads
External threads are found on the outside of a part. These include bolts, screws, and other fasteners. So, you can screw them into other objects.
Here are some examples
- Bolts
- threaded rods
- machine screws.
Internal Threads
These are threads found inside a hole. You can think of them as a nut or a tapped hole in a block.
The following are some examples:
- Threaded bushings
- Nuts
- Pipe
5. Standard Thread Types
Let us discuss some of the most popular mechanical thread shapes or profiles:
5.1 Unified Threads
- Common in: United States
- Shape: The angle of the thread is 60 degrees
- Types: Coarse and Fine
- Uses: Commonly for screws and bolts
You use unified threads mostly in machinery, cars, and general hardware.
5.2 Metric Threads
- They are used in International Systems
- It has a shape of 60 degrees and is measured in millimeters
- It can be divided into two types. These include coarse and fine
- These are used worldwide in machinery and electronics
So, metric threads are common in several parts of the world.
5.3 Acme Threads
- These have the shape of a trapezium.
- They are used in mechanisms and power transmissions.
- Its uses are in lead screws, vises, and presses
Acme threads are strong and smooth. So, they are ideal for moving parts.
5.4 Buttress Threads
- It has one flat side, while the other is angled.
- It can bear strong force or weight from one side.
- You use them in jacks, molding machines, or oil tools.
So, these threads can withstand forces and can be easily cleaned.
5.5 Square Threads
- These threads have the shape of a perfect square.
- You can move parts smoothly and accurately with these threads.
- These are used in actuators, lifting jacks, and machine tools.
This is the reason square threads are stronger. But they are hard to make and align.
5.6 Pipe Threads
- NPT, or National Pipe Thread, is mostly used in the United States
- BSP or British Standard Pipe is used internationally.
- There are several uses of it, such as plumbing, gas systems, oil & chemical pipes
Pipe threads are cut at a slight angle. This makes them fit tighter.
5.7 Trapezoidal Threads
- They have the shape of a trapezoid.
- They are used in European machinery
- It has various uses, such as lead screws or industrial equipment
These are similar to Acme threads but follow metric sizing.
6. Left-Hand vs Right-Hand Threads
The majority of threads are right-hand threads. So, they get tighter when you turn them clockwise. When you require rotation in the opposite direction, then left-hand threads are used.
Here are some examples of left-hand threads:
- Fan Blades
- Gas Cylinders
- Bike Pedals
7. Fine Threads vs Coarse Threads
| Feature | Fine Thread | Coarse Thread |
|---|---|---|
| Threads per inch | More | Fewer |
| Strength | Stronger in tension | Stronger in shear |
| Use in vibration | Less likely to loosen | More prone to loosen |
| Easier to strip? | Yes | No |
Fine threads are better for precision and space-saving, while coarse threads are easier to make and assemble.
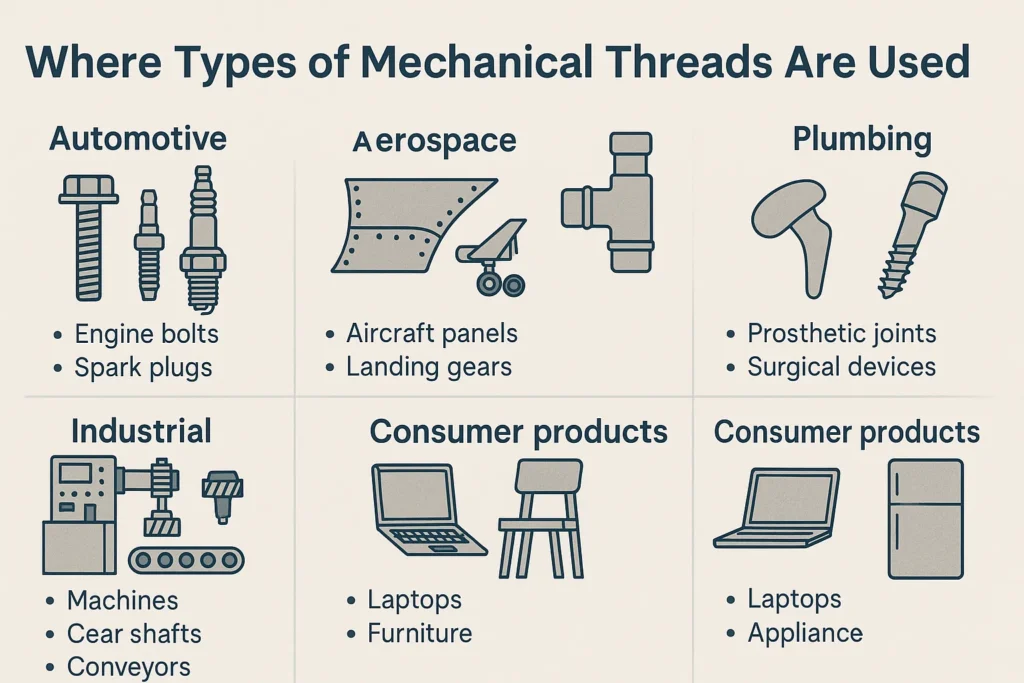
8. Where Types of Mechanical Threads Are Used
- In the automotive industry, they are used in engine bolts or spark plugs.
- Used in aircraft panels and landing gears in the aerospace industry.
- Pipe connectors or water fittings use mechanical threads
- Prosthetic joints or surgical devices use them in the medical field
- Also used in machines, gear shafts, or conveyers in industries
- Laptops, furniture, and appliances contain these threads
9. Picking the Right Thread Type
You have to consider the following steps when choosing the right thread:
- Load type: Is it best for holding and motion?
- Environment: You have to consider factors like heat, vibration, or corrosion
- Material: You also have to consider the material, such as metal or plastic.
- Standards: You can use regional or industry thread standards.
If you pick the wrong thread, then it can lead to damage, failure, or safety risks.
FAQs
Q1: Name the most common type of mechanical thread?
The most popular ones are unified and metric threads. Unified ones are common in the US, while metric ones are used worldwide.
Q2: What is the difference between external and internal threads?
You can say bolts have external threads as they are outside of the part. But internal threads like nuts are inside.
Q3: What are left-hand threads used for?
Left-hand threads are used when rotation would make a right-handed thread loose. This includes bike pedals or gas cylinders.
Q4: What is the strongest type of thread?
Square and acme threads are among the strongest ones. They are difficult to make.
Q5: Give a comparison between pipe and regular threads?
Sure, Pipe threads are created in a way that they seal tightly for gases and liquids. But regular threads are usually straight.
Q6: How can you repair damaged threads?
You can use thread repair kits, inserts like Heli-Coils, or even re-tap the hole. But the method to use depends on the damage.
Q7: Is it possible to differentiate a metric or unified thread?
You can use a thread gauge or compare the thread pitch. If the thread is in inches, then it is a unified thread. But if it is in millimeters, then it is a metric thread.
Q8: Do you know about thread pitch?
The distance between threads is what you call a thread pitch.
Summary
The various types of mechanical threads may look simple to you. But they are an important part of engineering and design. If you know about the types of mechanical threads, then you can pick the right one for your project. It also prevents failures and builds stronger and better machines. You need the best thread shape and size to make your design efficient and durable.





[…] are many tools used in mechanical inspection. Let’s explore them in simple […]
yeah bookmaking this wasn’t a high risk conclusion great post! .
you are my breathing in, I own few blogs and often run out from to post : (.