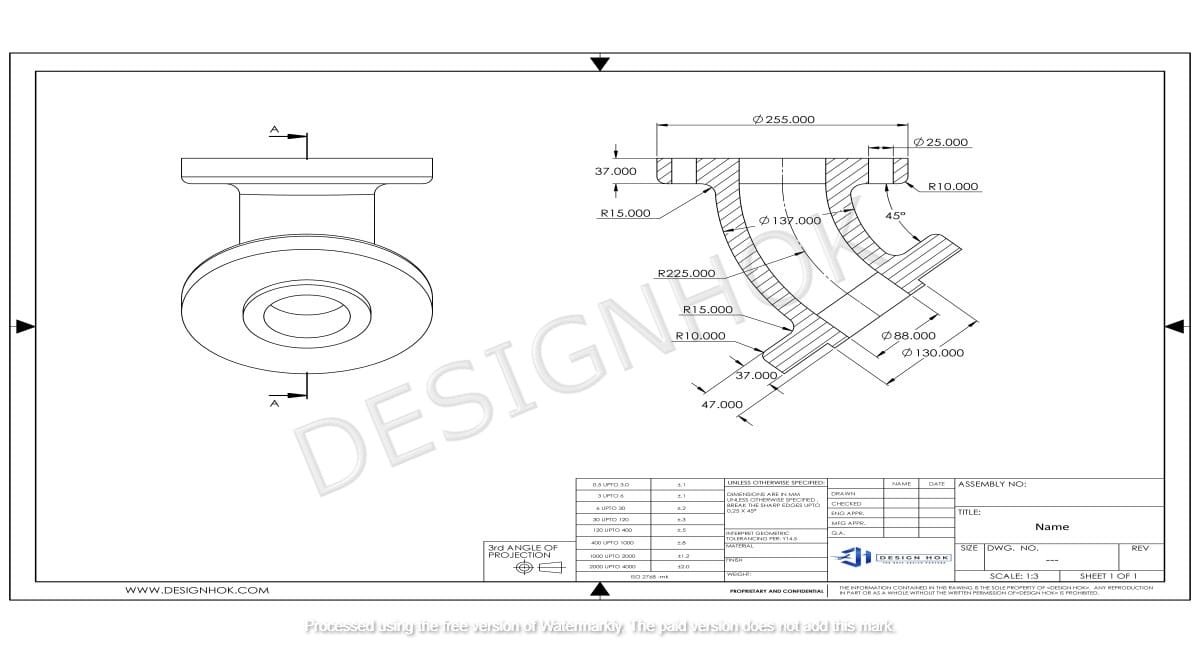
Role of 3D Modeling in the Engineering Design, from concept to production. The powerful tool enhances accuracy, efficiency, and innovation in engineering projects.
Introduction:
The Evolution Role of 3D Modeling in the Engineering Design
The engineering design process has undergone significant transformations over the years, largely due to advances in technology. Among these advancements, 3D modeling stands out as a game-changer, revolutionizing how engineers conceptualize, design, and develop products. Traditionally, engineers relied on 2D drawings and physical prototypes to visualize and test their designs. However, with the advent of Role of 3D Modeling in the Engineering Design in the Engineering Design Process, engineers now have a powerful tool that allows them to create detailed, accurate digital representations of their designs, significantly enhancing the entire design process. In this blog, we will explore the purpose of 3D modeling in the engineering design process, its benefits, and its impact on modern engineering practices.

The Purpose Role of 3D Modeling in the Engineering Design
Role of 3D Modeling in the Engineering Design serves several critical purposes in the engineering design process, each contributing to the overall success of a project. These purposes include:
1. Visualization of Concepts
One of the primary purposes of 3D modeling in engineering design is to visualize concepts clearly and accurately. Engineers can create detailed digital models that represent their ideas in three dimensions, allowing them to see how different components fit together, how they interact, and how the final product will look. This level of visualization is essential for identifying potential design flaws early in the process and ensuring that the final product meets all requirements.
2. Enhanced Communication
Engineering projects often involve collaboration between multiple teams, including design, manufacturing, and marketing. 3D models provide a common visual language that all stakeholders can understand, regardless of their technical background. This enhanced communication helps ensure that everyone involved in the project is on the same page, reducing misunderstandings and streamlining the decision-making process.
3. Design Optimization
Role of 3D Modeling in the Engineering Design allows engineers to experiment with different design iterations quickly and efficiently. By making changes to the digital model, engineers can assess the impact of those changes on the overall design, optimizing for factors such as weight, strength, and cost. This iterative process helps engineers arrive at the best possible design before moving on to the production phase.
4. Simulation and Testing
Another significant purpose of Role of 3D Modeling in the Engineering Design is to facilitate simulation and testing. Engineers can use Role of 3D Modeling in the Engineering Design to run simulations that mimic real-world conditions, such as stress tests, thermal analysis, and fluid dynamics. These simulations provide valuable insights into how the product will perform under various conditions, allowing engineers to make informed decisions and refine their designs before creating physical prototypes.
5. Prototyping and Manufacturing
Once the design has been optimized and tested, Role of 3D Modeling in the Engineering Design plays a crucial role in the prototyping and manufacturing stages. Engineers can use the digital model to create physical prototypes through techniques like 3D printing or CNC machining. These prototypes can be used for further testing and validation before the final product is manufactured. Additionally, the digital model can be directly integrated into the manufacturing process, ensuring that the final product is produced with the highest level of accuracy and precision.
6. Documentation and Compliance
Role of 3D Modeling in the Engineering Design also serve as valuable documentation for the entire engineering design process. They provide a comprehensive record of the design, including all specifications, dimensions, and materials used. This documentation is essential for ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations, as well as for future reference in case any modifications or repairs are needed.

The Benefits of Role of 3D Modeling in Engineering Design
The use of 3D modeling in the engineering design process offers numerous benefits, which include:
1. Improved Accuracy and Precision
3D Modeling in the Engineering Design Process allows engineers to create highly detailed and accurate representations of their designs, reducing the likelihood of errors and inconsistencies. This level of precision is particularly important in industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing, where even the smallest mistake can have significant consequences.
2. Increased Efficiency
By allowing engineers to visualize, test, and optimize their designs digitally, 3D modeling significantly reduces the time and resources needed to bring a product from concept to production. This increased efficiency translates to faster project completion times and reduced costs, making 3D modeling an invaluable tool in today’s competitive engineering landscape.
3. Enhanced Collaboration
As mentioned earlier, 3D models provide a common visual language that facilitates communication and collaboration among different teams. This enhanced collaboration leads to better decision-making, fewer misunderstandings, and a more streamlined design process.
4. Greater Innovation
The ability to quickly iterate on designs and explore different possibilities encourages innovation in engineering. Engineers can experiment with new ideas, materials, and configurations without the constraints of traditional 2D drawings or physical prototypes. This freedom to innovate often leads to more creative and effective solutions to engineering challenges.
5. Better Quality Control
Role of 3D Modeling in the Engineering Design enables engineers to identify and address potential issues before they become problems in the physical product. By catching these issues early in the design process, engineers can ensure that the final product meets the highest quality standards, reducing the risk of costly recalls or redesigns.
The Impact of Role of 3D Modeling in the Engineering Design Practices
The widespread adoption of Role of 3D Modeling in the Engineering Design has had a profound impact on modern engineering practices. It has transformed how engineers approach the design process, leading to more efficient, accurate, and innovative solutions. Here are a few examples of how 3D modeling has influenced different engineering fields:
1. Automotive Engineering
In the automotive industry, 3D modeling has revolutionized the design and development of vehicles. Engineers can create detailed digital models of entire cars, including all individual components, and simulate how they will perform under various conditions. This ability to test and optimize designs in a virtual environment has led to the development of safer, more efficient, and more reliable vehicles.
2. Aerospace Engineering
Aerospace engineers rely heavily on Role of 3D Modeling in the Engineering Design to design aircraft, spacecraft, and their components. The precision and accuracy offered by 3D modeling are essential in an industry where even minor deviations can have catastrophic consequences. Additionally, 3D modeling allows aerospace engineers to simulate the effects of extreme conditions, such as high-speed flight or re-entry into the Earth’s atmosphere, ensuring that their designs can withstand these challenges.
3. Civil Engineering
In civil engineering, Role of 3D Modeling in the Engineering Design is used to design and visualize large-scale infrastructure projects, such as bridges, tunnels, and buildings. By creating detailed digital models, civil engineers can assess the feasibility of their designs, identify potential issues, and optimize for factors like structural integrity, cost, and environmental impact. This ability to visualize and test designs before construction begins has led to more efficient and sustainable infrastructure projects.
4. Medical Device Engineering
In the medical field, 3D modeling has become a critical tool for designing and developing medical devices, such as implants, prosthetics, and surgical instruments. Engineers can create highly detailed models of these devices, simulate their performance in the human body, and optimize their designs for safety and efficacy. This use of 3D modeling has led to the development of more effective and customized medical devices, improving patient outcomes.
Conclusion:
The Future of Role of 3D Modeling in the Engineering Design
As technology continues to advance, the Role of 3D Modeling in the Engineering Design will only become more significant. Emerging technologies, such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and artificial intelligence (AI), are expected to further enhance the capabilities of 3D modeling, enabling even more accurate, efficient, and innovative design solutions. For engineers, mastering 3D modeling is no longer optional but essential for staying competitive in today’s rapidly evolving engineering landscape. By leveraging the power of 3D modeling, engineers can continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, creating products and solutions that meet the highest standards of quality, performance, and innovation.
FAQs
1. What is the primary purpose of 3D modeling in engineering design?
The primary purpose of 3D modeling in engineering design is to visualize, test, and optimize designs in a digital environment, allowing engineers to create accurate and efficient products before moving on to physical prototypes and manufacturing.
2. How does 3D modeling improve communication in engineering projects?
3D models provide a common visual language that all stakeholders can understand, facilitating better communication and collaboration among different teams involved in the project.
3. What are the benefits of using 3D modeling in the engineering design process?
The benefits of using 3D modeling include improved accuracy and precision, increased efficiency, enhanced collaboration, greater innovation, and better quality control.
4. How does 3D modeling contribute to design optimization?
3D modeling allows engineers to quickly iterate on designs, making changes and assessing their impact in real-time. This iterative process helps engineers optimize their designs for factors like weight, strength, and cost.
5. In which industries is 3D modeling particularly important?
3D modeling is particularly important in industries such as automotive, aerospace, civil engineering, and medical device engineering, where precision, accuracy, and innovation are critical.
6. What role does 3D modeling play in prototyping and manufacturing?
3D modeling plays a crucial role in prototyping by allowing engineers to create digital models that can be used to produce physical prototypes through techniques like 3D printing. These models are also integrated into the manufacturing process to ensure accurate production.
7. How will emerging technologies impact the future of 3D modeling in engineering?
Emerging technologies like AR, VR, and AI are expected to enhance the capabilities of 3D modeling, making it even more accurate, efficient, and innovative, further transforming the engineering design process.