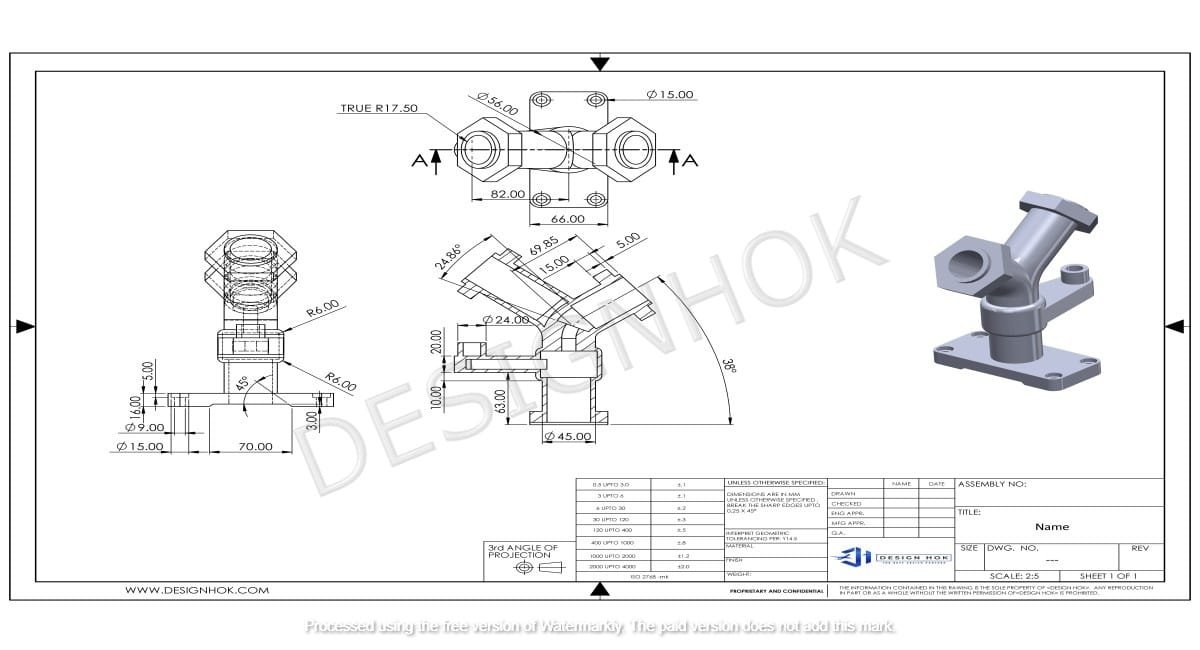
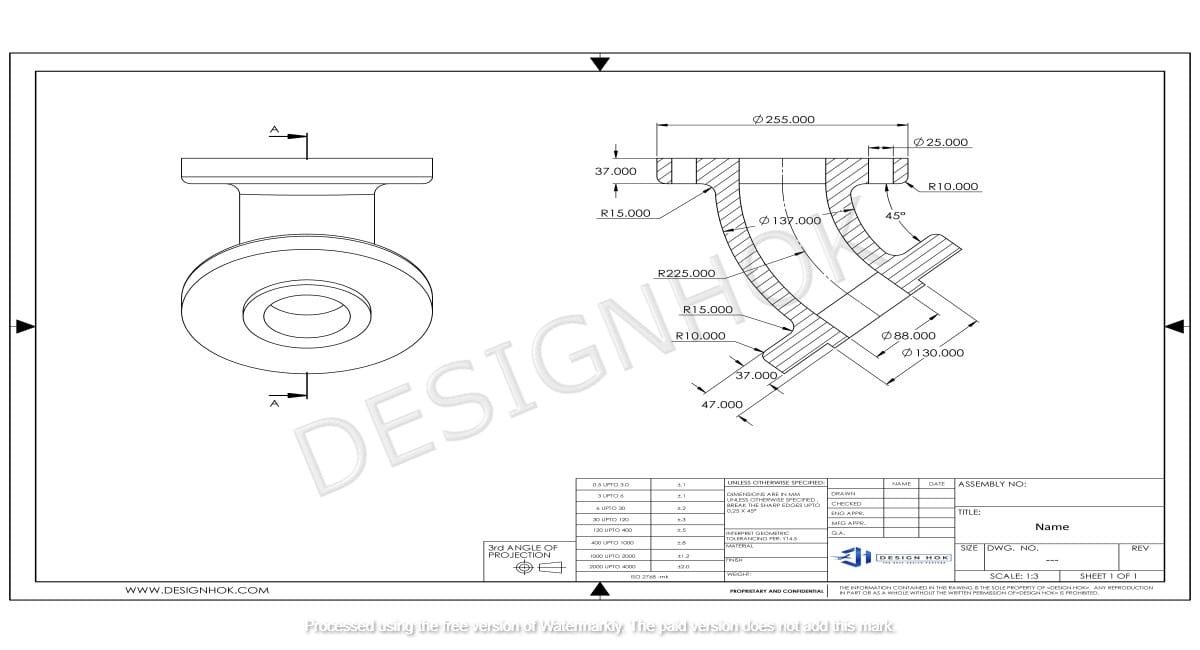
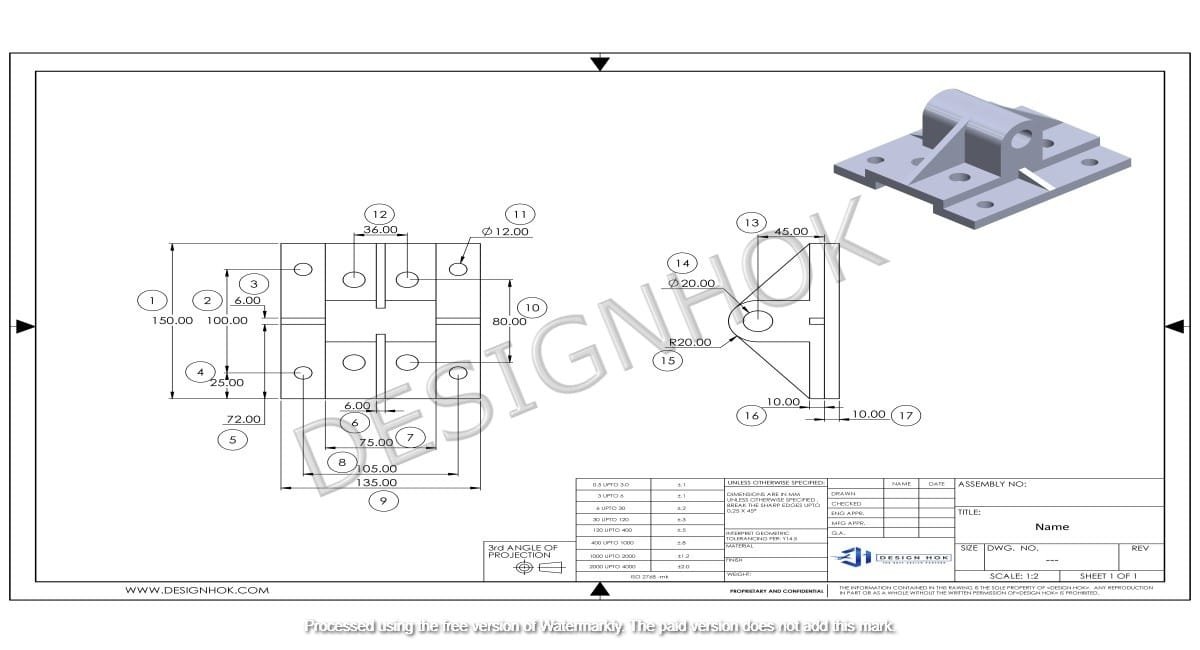
3D rendering is a crucial process in modern design and visualization, and it plays a vital role in creating lifelike representations of 3D models. For DesignHOK, a company known for its excellence in design services, rendering serves as a powerful tool to transform ideas into visual masterpieces. This article delves into the fundamentals of rendering in 3D modeling, its significance, techniques, and its application in DesignHOK’s projects.
What is Rendering in 3D Modeling?
3D rendering refers to the process of creating two-dimensional images or animations from a 3D model using computer software. It is a bridge between abstract 3D data and visually compelling outputs that mimic reality. At its core, rendering involves computing and transforming the information in a 3D scene—such as geometry, lighting, and textures—into an image or video format.
How Enhances Rendering in 3D Modeling
Rendering breathes life into 3D models. While a 3D model defines the shape and structure, rendering adds elements like texture, color, light, and shadow, making the design visually appealing. For DesignHOK, this process is crucial in showcasing detailed representations that clients can easily comprehend.
Types of Rendering in 3D Modeling
Real-Time Rendering
Real-time rendering is often used in applications like gaming and virtual reality. It prioritizes speed, enabling visuals to update instantaneously as the scene changes.
Offline Rendering
Offline rendering focuses on achieving photorealistic results. It’s commonly used in architectural visualization and product design, where quality is more critical than speed.
Key Elements in Rendering in 3D Modeling
- Textures and Materials
These define the surface qualities of an object, like roughness, gloss, or transparency. - Lighting Techniques
Proper lighting sets the mood and enhances realism, whether it’s ambient, directional, or spot lighting. - Camera Positioning
The camera’s angle and settings determine the viewer’s perspective and focus areas.
Rendering in 3D Modeling Techniques
Ray Tracing
Simulates the way light interacts with objects, creating realistic shadows and reflections.
Rasterization
A faster technique that converts 3D objects into a 2D image without as much computational demand.
Global Illumination
Accounts for indirect lighting, adding depth and realism to scenes.
Software Used for Rendering in 3D Modeling
Some popular rendering tools include:
- Blender: Open-source and versatile.
- Autodesk 3ds Max: Common in architectural visualization.
- V-Ray: Known for photorealistic output.
DesignHOK often employs these tools to achieve professional-grade results.
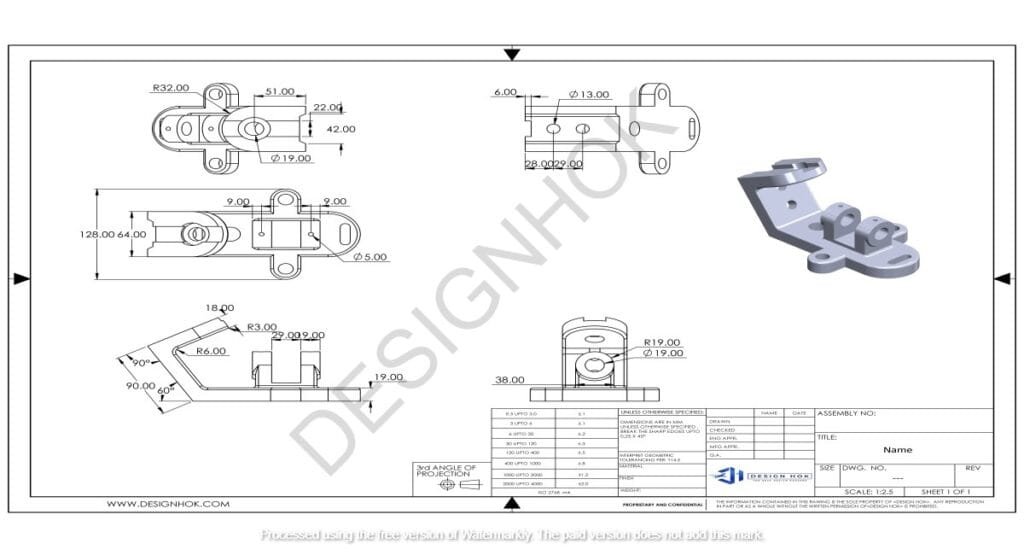
The Rendering Workflow
Rendering starts with modeling, where the basic structure is created. Next, textures, lighting, and other details are added before rendering the final image or animation. Iteration ensures the output meets quality standards.
Applications of Rendering in 3D Modeling
Architectural Visualization
Rendering helps visualize buildings and interiors, ensuring accurate spatial understanding.
Product Design
From gadgets to machinery, rendered visuals illustrate the design concept in detail.
Engineering Prototypes
Rendering allows clients to see how mechanical parts fit and function before physical production.
Benefits of Rendering in 3D Modeling
- Time Efficiency: Faster project approvals due to clear visuals.
- Cost Savings: Reduces the need for physical prototypes.
- Improved Communication: Bridges the gap between designers and clients.
Challenges in Rendering in 3D Modeling
Rendering can be time-consuming, particularly for high-quality outputs. It also requires advanced hardware to handle complex scenes efficiently.
Future of Rendering in 3D Modeling
Emerging trends like real-time rendering and integration with AR/VR are set to revolutionize how designs are presented, making the process more interactive and immersive.
Why Rendering is Essential for DesignHOK
For DesignHOK, rendering ensures projects stand out with exceptional quality and attention to detail. It enhances client satisfaction and upholds the company’s reputation for delivering top-notch design solutions.
Tips for Better Rendering
- Simplify your scenes to reduce rendering time.
- Experiment with different lighting setups.
- Always use high-quality textures for realistic results.
Conclusion
3D rendering is a cornerstone of modern design practices, offering a seamless way to transform concepts into tangible visuals. For DesignHOK, it enables accurate representations and effective communication with clients. By leveraging cutting-edge rendering techniques, DesignHOK continues to excel in delivering high-quality projects.
FAQs
1. What is the purpose of 3D rendering in design?
3D rendering provides realistic visuals that help in understanding and communicating design concepts effectively.
2. How does DesignHOK use rendering in its projects?
DesignHOK uses rendering for architectural visualization, product design, and engineering prototypes to deliver detailed, photorealistic outputs.
3. What tools are commonly used for 3D rendering?
Popular tools include Blender, Autodesk 3ds Max, and V-Ray, among others.
4. Why is lighting important in rendering?
Lighting enhances realism by adding depth, mood, and focus to the rendered scene.
5. Is 3D rendering time-consuming?
Yes, especially for high-quality renders, but optimized workflows and powerful hardware can reduce time significantly.