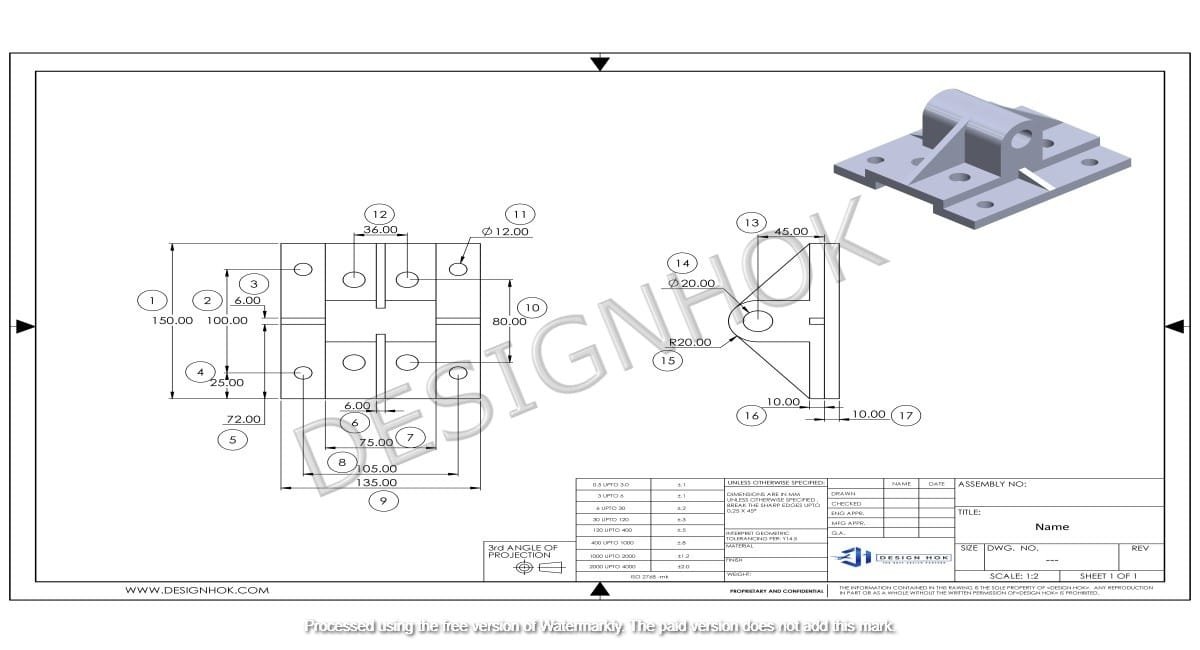
In the world of engineering and design, precision and clarity are vital. The introduction of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) has revolutionized how these drawings are created and utilized. One of the most fundamental aspects of CAD is the creation of 2D drawings. These drawings serve various critical purposes in industries ranging from architecture to manufacturing. In this blog, we will dive deep into the purpose of 2D drawings in CAD, exploring their benefits, applications, and importance in the design process.
What Are Purpose of 2D Drawings in CAD?
2D drawings in CAD refer to flat, two-dimensional representations of objects and structures. Unlike 3D models, which provide depth and volume, 2D drawings focus on the shape, dimensions, and layout of an object. They typically include elements like lines, arcs, circles, and text annotations to represent various features of a design.
In CAD software, 2D drawings are typically the first step in the design process, providing a visual guide for building more complex 3D models or serving as the final product when a 3D model isn’t necessary. These drawings can range from simple sketches to detailed, dimensioned technical blueprints used for manufacturing and construction.
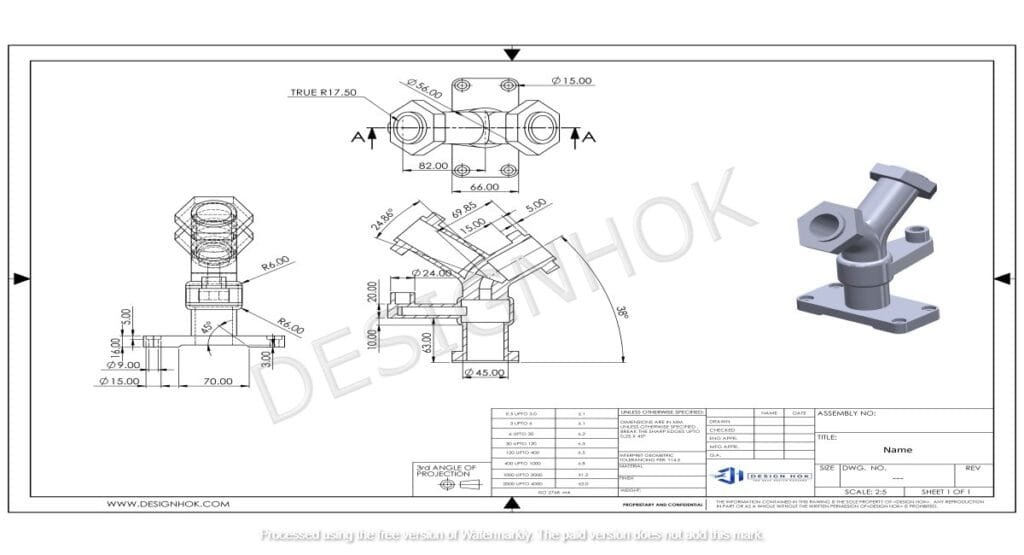
Purpose of 2D Drawings in CAD
1. Accurate Communication
One of the primary purposes of 2D drawings in CAD is to communicate a design clearly and precisely. These drawings act as a visual language between designers, engineers, manufacturers, and clients. Since most technical information is represented through symbols, annotations, and dimensions, CAD 2D drawings can eliminate misunderstandings, ensuring that everyone involved in the project is on the same page.
For example, in architecture, a 2D drawing of a building layout ensures that all the details, such as wall dimensions, door placements, and window heights, are accurately conveyed. This clarity is vital, as construction cannot proceed without a clear understanding of the design.
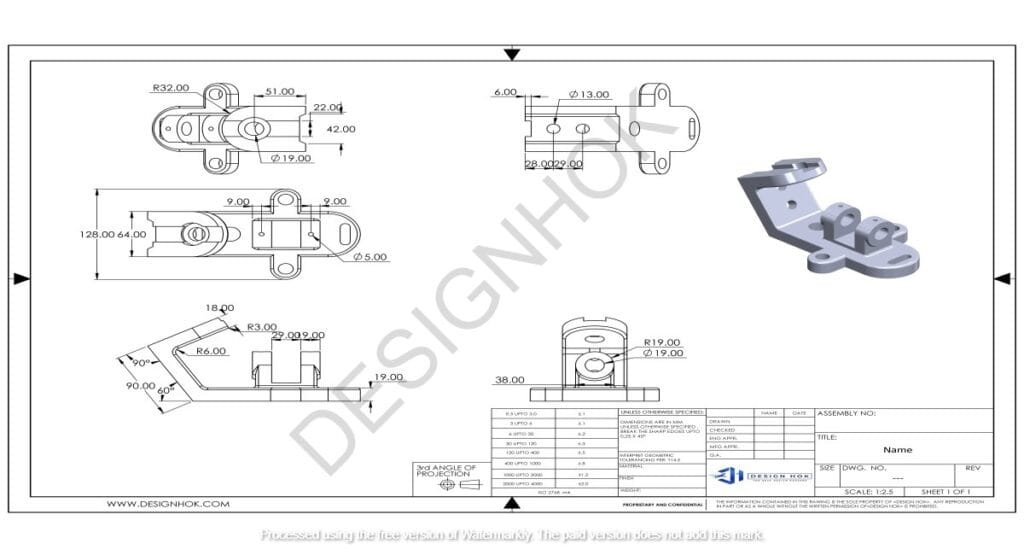
2. Precision and Accuracy
CAD software allows for high precision in creating Purpose of 2D Drawings in CAD. Manual drafting can sometimes introduce human error, leading to inaccuracies. However, in CAD, designers can specify exact measurements and angles, ensuring that every part of the drawing is accurate to the finest detail. This level of precision is essential in industries where tight tolerances and exact specifications are required, such as manufacturing and engineering.
For example, when designing a machine part, even the smallest deviation in a Purpose of 2D Drawings in CAD can affect how well the part fits with other components. CAD ensures that all parts fit together correctly by providing an exact blueprint.
3. Standardization
In industries such as manufacturing and construction, standardization is essential. 2D CAD drawings follow established standards and conventions, making it easier to understand and use the drawings across different teams, departments, and organizations. These standards include conventions for line thickness, dimensioning styles, and symbols, which make the drawings consistent and easy to interpret.
For instance, in engineering, standardized Purpose of 2D Drawings in CAD are used universally to ensure that a design can be understood by anyone familiar with the system, regardless of language or location.
4. Quick Modifications
One of the biggest advantages of using CAD for 2D drawings is the ease of making changes. Unlike traditional hand-drawn blueprints, CAD files can be easily edited, updated, or revised without starting over from scratch. If a design modification is needed, engineers and designers can simply alter the relevant sections of the drawing and update the dimensions or annotations accordingly.
For example, if a building’s layout needs to be adjusted due to changes in regulations or customer preferences, the 2D CAD drawing can be quickly altered to reflect these changes, saving time and effort.
5. Efficiency and Time-Saving
Purpose of 2D Drawings in CAD are faster to create than their hand-drawn counterparts. With the ability to reuse elements, copy and paste components, and quickly apply dimensions, CAD software streamlines the design process. This time efficiency is particularly important in fast-paced industries, where meeting deadlines and staying within budget are critical.
The automation features in CAD also allow for quicker updates and modifications. For example, if multiple drawings for different parts of a project need to be adjusted, CAD tools can automatically update related sections, ensuring consistency across all drawings without manual revisions.
6. Detailing for Manufacturing
2D drawings are often used as blueprints for manufacturing processes. They provide detailed information on the shape, size, material specifications, and assembly instructions for parts or products. These drawings are crucial in ensuring that the final product matches the original design.
In manufacturing, for example, a Purpose of 2D Drawings in CAD of a part might include precise dimensions, material properties, and instructions for assembly or installation. This helps the manufacturer create the part exactly as intended, avoiding costly mistakes and delays in the production process.
7. Legal Documentation
In many industries, Purpose of 2D Drawings in CAD serve as legal documents that define the scope of work, materials, and procedures. In construction, these drawings are often used in contracts to ensure that all parties are aligned on the project details. Any discrepancies between the design and the final build can lead to legal disputes, so having clear, well-documented 2D CAD drawings is essential for protecting the in terests of all stakeholders.
8. Basis for 3D Modeling
While 3D models are often the final product in many design projects, Purpose of 2D Drawings in CAD are typically the foundation for building these models. They provide the necessary measurements, constraints, and details needed to create accurate 3D representations of an object or system.
Engineers and designers often start with 2D sketches or drawings, which they then use as references when creating more complex 3D models. This process is crucial in ensuring that the final 3D model is both accurate and functional.
Applications of 2D Drawings in CAD
2D drawings in CAD are used in various industries, including:
- Architecture: To create building layouts, floor plans, and elevations.
- Engineering: For designing mechanical parts, electrical circuits, and systems.
- Manufacturing: To create parts and assembly diagrams for production.
- Construction: To define the scope of work and ensure accurate project execution.
Conclusion
The purpose of 2D drawings in CAD is fundamental to modern design and engineering. These drawings provide clarity, precision, and efficiency, helping designers, engineers, and manufacturers collaborate effectively. They are essential tools for communication, ensuring that designs are accurately represented and understood. With CAD, 2D drawings are more than just basic representations—they are precise, reliable blueprints that drive innovation in industries worldwide.
FAQs
Why are 2D CAD drawings important in manufacturing?
2D CAD drawings provide detailed and accurate information about the dimensions and specifications of parts, which helps manufacturers produce them correctly.
How does 2D CAD differ from 3D CAD?
2D CAD represents objects in two dimensions, focusing on shape and size, while 3D CAD adds depth and volume, creating realistic models of objects.
Can 2D CAD drawings be used for both design and construction?
Yes, 2D CAD drawings are widely used in both design and construction to communicate the exact specifications and dimensions of a project.
How do CAD tools improve the accuracy of 2D drawings?
CAD software allows for precise measurements and automated features, reducing human error and ensuring accurate drawings every time.
What industries benefit from using 2D CAD drawings?
Many industries, including architecture, engineering, manufacturing, and construction, benefit from the precision, efficiency, and clarity that 2D CAD drawings provide.