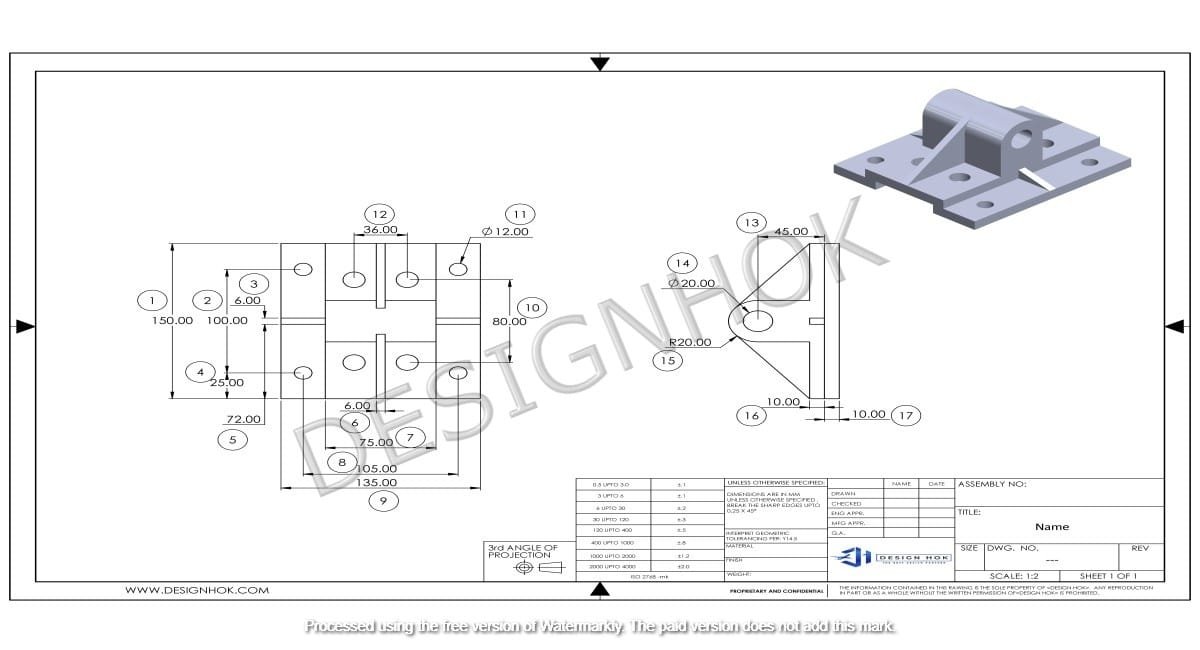
Description
Precision design in aerospace engineering is essential for ensuring safety, performance, and regulatory compliance. When paired with AS 9100 certification, it reflects the highest standard of quality management in the aerospace sector. In this article, we explore how precision engineering aligns with AS 9100, why it matters, and how manufacturers can excel in an industry where there’s no room for error.
1. What Is Precision Design for Aerospace?
Precision Design for Aerospace refers to the detailed and accurate development of components and systems in aerospace that meet strict tolerances and performance standards. It encompasses everything from CAD modeling to materials selection, stress testing, and prototyping.
In the aerospace industry, microscopic inaccuracies can lead to catastrophic failures. Therefore, precision isn’t just preferred—it’s absolutely critical.
Related NLP terms:
- aerospace component tolerances
- high-precision aerospace manufacturing
- CAD for aviation systems
2. Understanding AS 9100 Certification
AS 9100 is an international quality management system (QMS) standard specifically created for thePrecision Design for Aerospace, aviation, and defense industries. Based on ISO 9001, AS 9100 adds additional safety, risk, and traceability requirements.
To be AS 9100 certified, an organization must demonstrate strict adherence to Precision Design for Aerospace:
- Documented quality processes
- Design control and configuration management
- Risk-based thinking and product safety
- Supplier performance tracking
- Continuous improvement practices
AS 9100 is issued by accredited certification bodies and requires routine audits.
3. Why Precision Design Must Be AS 9100 Certified
Precision design without standardized processes risks non-conformance, safety hazards, and rework. AS 9100 certification ensures that every design process in Precision Design for Aerospace:
- Meets customer and regulatory expectations
- Reduces human error
- Follows a traceable documentation trail
- Minimizes design-related defects
This certification proves a manufacturer’s commitment to excellence and risk mitigation, essential for aerospace clients like Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and SpaceX.
AI Overview–Optimized Answer:
Precision aerospace design must be AS 9100 certified to meet the industry’s quality, safety, and traceability requirements.
4. Key AS 9100 Requirements for Design and Engineering
AS 9100 includes design-specific clauses critical to aerospace manufacturing:
a. Design and Development Planning
Teams must define project stages, responsible personnel, and verification/validation methods.
b. Design Inputs
Specifications must include regulatory, functional, and customer-driven needs.
c. Design Outputs
Final designs must be complete, verifiable, and able to meet input requirements.
d. Design Review
Multiple reviews should occur during development to identify and correct issues early.
e. Verification and Validation
Every design must undergo testing and simulation to ensure real-world function and compliance.
f. Design Change Control
Any modifications must follow a documented process to avoid unauthorized changes.
These clauses create a closed-loop system for design control, boosting traceability and reducing error rates.
5. The Role of Quality Management in Aerospace Precision
AS 9100 requires a robust Quality Management System (QMS) that integrates with precision design activities. Here’s how QMS enhances design:
- Process Control: Ensures that design processes are repeatable and measurable in Precision Design for Aerospace.
- Risk Mitigation: Prevents design flaws through structured hazard analysis.
- Documentation: Provides clear records for design decisions and changes.
- Internal Audits: Helps spot design deviations before products reach production.
By embedding QMS into the design workflow, manufacturers can ensure zero-defect output—a critical requirement in aerospace.
6. Steps to Achieve AS 9100-Certified Precision Design for Aerospace
- Perform a Gap Analysis: Evaluate your current design and QMS processes against AS 9100 requirements.
- Develop Design Procedures: Create standardized, document-controlled steps for planning, verification, and approval in Precision Design for Aerospace.
- Train Design Teams: Ensure all team members understand their responsibilities under AS 9100.
- Implement Design Reviews: Formalize the design approval process.
- Conduct Internal Audits: Continuously monitor design-related metrics and compliance.
- Engage a Certifying Body: Choose an accredited registrar for external audits.
- Maintain and Improve: Use customer feedback and audit results to refine processes.
7. Benefits of Combining Precision Design with AS 9100
a. Competitive Advantage
Clients prefer suppliers who meet global aerospace standards in Precision Design for Aerospace.
b. Enhanced Product Safety
AS 9100 ensures safety is built into every stage of design.
c. Process Efficiency
Standardized design practices reduce cycle times and errors.
d. Higher Customer Confidence
Certifications instill trust in government agencies and private sector clients alike.
e. Easier Market Entry
Many aerospace tenders require AS 9100 as a baseline for eligibility.
8. Real-World Aerospace Applications
Examples of precision design in AS 9100-certified projects include:
- Jet engine components with sub-micron tolerances
- Satellite structures designed to withstand space temperatures
- Avionics systems where signal interference is minimized through precision enclosure design
- Landing gear systems with fatigue-tested in Precision Design for Aerospace
- Flight control systems that depend on 3D-modeled precision assemblies
Each application demands rigorous attention to detail and strict design validation, enforced through AS 9100 standards.
9. Maintaining AS 9100 Compliance in Design
AS 9100 isn’t a “once-and-done” certification. Manufacturers must:
- Conduct annual surveillance audits
- Review and update design processes regularly
- Document changes with full traceability
- Train new engineers on compliance procedures
- Integrate lessons from non-conformance reports into design updates
Maintaining certification ensures that your design processes evolve with industry standards and customer expectations.
10. Conclusion
In the aerospace industry, Precision Design for Aerospace is not optional—it’s mission-critical. AS 9100 certification ensures that design processes are safe, reliable, and globally trusted. By combining both, manufacturers can achieve quality excellence, unlock global contracts, and drive innovation with confidence.
A company that delivers AS 9100-certified precision design proves to its clients that it is not only technically capable but also strategically prepared to deliver performance under pressure.
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the difference between ISO 9001 and AS 9100 in aerospace design?
ISO 9001 is a general quality standard, while AS 9100 includes aerospace-specific requirements such as risk analysis, design verification, and traceability. For aerospace design, AS 9100 is the required benchmark.
Q2: How does AS 9100 improve precision in aerospace design?
AS 9100 enforces rigorous design planning, review, verification, and change control processes, all of which reduce errors and ensure high-precision outcomes.
Q3: Is AS 9100 certification required for all aerospace manufacturers?
It is not legally mandatory, but most aerospace clients require suppliers to be AS 9100 certified to ensure consistent quality and risk control.
Q4: Can small design firms become AS 9100 certified?
Yes. Small and medium-sized firms can tailor a scalable Quality Management System that meets AS 9100 standards while maintaining flexibility.
Q5: How often must AS 9100 certification be renewed?
Full re-certification is typically required every three years, with annual surveillance audits to ensure continued compliance.