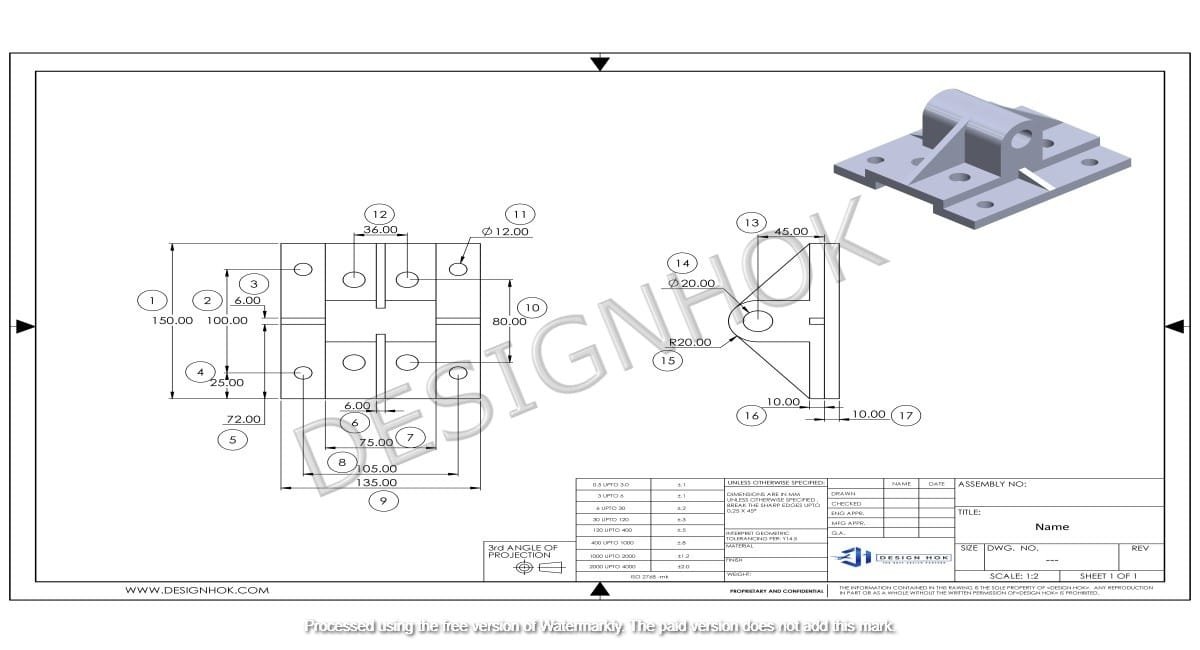
Exploring 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts has revolutionized the way machine parts are designed, analyzed, and manufactured. This blog explores the importance of 3D modeling for different machine parts, how it enhances precision, and its impact on modern engineering design.
Introduction:
The Rise of Exploring 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts: Precision and Innovation in Design
The design and manufacturing of machine parts have significantly evolved with the advancement of 3D modeling. Traditionally, engineers relied on 2D technical drawings and physical prototypes to create and test machine components. However, 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts of Different Machine Parts has transformed this process by offering a more precise, flexible, and efficient method for visualizing, designing, and refining machine parts. By creating digital representations of components, engineers can simulate performance, optimize designs, and reduce errors before manufacturing begins. In this blog, we will dive deep into the importance of 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts of Different Machine Parts for different machine parts and how it is shaping the future of engineering.
The Role of 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts
Exploring 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts plays an essential role in the design and development of machine parts across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, industrial equipment, and consumer goods. Here’s how it contributes to each stage of the design process:
1. Conceptualization and Visualization
Before any physical part is produced, the idea must be visualized. 3D modeling enables designers and engineers to turn their initial concepts into digital models, providing a comprehensive view of the part from multiple angles. This allows stakeholders to understand the geometry, proportions, and spatial relationships between components, which is critical in determining whether the part will fit within the larger system.
For example, when designing a gear system, Exploring 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts can visually represent how individual gears interact with one another, allowing engineers to identify potential issues such as interference or misalignment.
2. Precision in Design and Engineering
One of the greatest advantages of Exploring 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts is the precision it offers. Engineers can define exact measurements, tolerances, and material properties, ensuring that every detail of the part is accurately represented. This level of precision reduces the likelihood of errors during production and ensures that the part will function as intended in real-world applications.
For instance, in the design of an engine block, precise measurements are crucial to ensure that the pistons move smoothly within the cylinders and that all components fit together tightly without gaps or misalignments. 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts allow for these precise calculations and make adjustments as needed before production.
3. Simulation and Performance Testing
Before committing to physical prototypes, engineers use Exploring 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts to simulate the performance of machine parts under real-world conditions. This can include testing for factors such as stress, heat, and vibration. By analyzing how the part behaves under different loads and environments, engineers can make informed decisions about design improvements and material selection.
For example, a turbine blade designed for an aircraft engine can be subjected to simulated aerodynamic forces in the 3D model, allowing engineers to see how it will perform at high speeds and under extreme temperatures. This reduces the risk of failure in actual operation.
4. Iterative Design and Optimization
Exploring 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts makes it easy to iterate and refine designs. Engineers can quickly make modifications to the model, test different configurations, and optimize the part for performance, weight, and cost. This flexibility is particularly valuable when working on complex machine parts that require multiple revisions before reaching the final design.
Take, for example, the design of a transmission system. Engineers can use 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts to test different gear ratios, material strengths, and lubrication systems, ensuring that the final design maximizes efficiency while minimizing wear and tear.
5. Manufacturing and Prototyping
Once the design is finalized, Exploring 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts are used to generate detailed manufacturing instructions. These models provide precise data for machining, assembly, and quality control, ensuring that the part can be produced accurately and efficiently.
3D models can also be used to create rapid prototypes, which are physical representations of the part created through additive manufacturing (such as 3D printing). Prototyping allows engineers to test the part in real-world conditions and make any final adjustments before mass production begins.

6. Collaboration and Communication
Exploring 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts act as a universal language for engineers, designers, and manufacturers. They provide a visual and interactive way to communicate complex ideas and design requirements, enabling teams to collaborate more effectively. With Exploring 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts, stakeholders can explore the part in a virtual environment, provide feedback, and make design changes in real-time.
In large-scale projects, such as the design of industrial machinery or automotive components,3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts improves collaboration by ensuring that everyone involved has a clear understanding of the part’s specifications and functionality.
Examples of Exploring 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts
Exploring 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts is widely used across different industries to design and optimize machine parts. Here are a few examples:
1. Gears and Gear Systems
Gears are essential components in various machines, from simple devices like clocks to complex systems like automotive transmissions. 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts allows engineers to create highly detailed gear profiles, test how they interact with each other, and ensure smooth transmission of motion and torque.
2. Bearings
Bearings reduce friction between moving parts in machines, such as rotating shafts. Exploring 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts is crucial in designing bearings to meet specific load, speed, and durability requirements. Engineers can simulate wear patterns, temperature changes, and lubrication needs in the model to optimize performance.
3. Pistons and Cylinders
In engines, the piston and cylinder are critical for converting energy into motion. Using 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts, engineers can design pistons with precise tolerances, ensuring they fit perfectly within the cylinders to maximize efficiency and minimize friction.
4. Turbine Blades
Turbine blades are used in jet engines and power plants to convert energy from fluids into mechanical power. Exploring 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts helps engineers design blades with aerodynamic profiles, simulate the forces acting on them, and test their performance under extreme conditions like high temperatures and pressures.
5. Shafts and Axles
Shafts and axles are components that transfer torque and rotation between different parts of a machine. 3D modeling ensures that shafts are designed with the correct dimensions and material properties to handle the required loads and speeds without failure.
Conclusion:
The Future of Exploring 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts
3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts has revolutionized the design and manufacturing of machine parts, offering unparalleled precision, flexibility, and efficiency. It allows engineers to visualize complex components, test their performance, and optimize designs before moving to production. As technology continues to evolve, Exploring 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts will become even more integrated into the engineering process, enabling faster development times, reduced costs, and higher-quality machine parts.
Whether designing gears, pistons, or turbine blades, Exploring 3D Modeling of Different Machine Parts empowers engineers to create innovative solutions that push the boundaries of what’s possible in machine design. By embracing this technology, industries can continue to improve their products and remain competitive in a rapidly changing world.
FAQs
1. What is 3D modeling in machine part design?
3D modeling is the process of creating a three-dimensional digital representation of machine parts. It is used to visualize, design, and test components before they are manufactured, ensuring precision and accuracy in the final product.
2. How does 3D modeling improve the design of machine parts?
3D modeling improves design by offering detailed visualization, allowing for precise measurements, enabling performance simulations, and facilitating iterative design processes. It helps engineers optimize machine parts for functionality, durability, and cost-efficiency.
3. What types of machine parts benefit from 3D modeling?
Various machine parts benefit from 3D modeling, including gears, bearings, pistons, cylinders, turbine blades, shafts, and axles. Each part can be designed with high precision to meet specific performance requirements.
4. Can 3D modeling be used for prototyping machine parts?
Yes, 3D models are often used to create rapid prototypes through 3D printing or other additive manufacturing techniques. Prototyping allows engineers to test the part in real-world conditions and make adjustments before full-scale production.
5. How does 3D modeling help in collaboration during the design process?
3D models provide a visual representation of the design, making it easier for engineers, designers, manufacturers, and stakeholders to collaborate. They enable real-time feedback, design changes, and ensure that everyone involved understands the specifications of the part.
6. What software is commonly used for 3D modeling in machine part design?
Popular software includes SolidWorks, AutoCAD, CATIA, Siemens NX, and PTC Creo. These tools offer advanced features for designing, simulating, and analyzing machine parts.