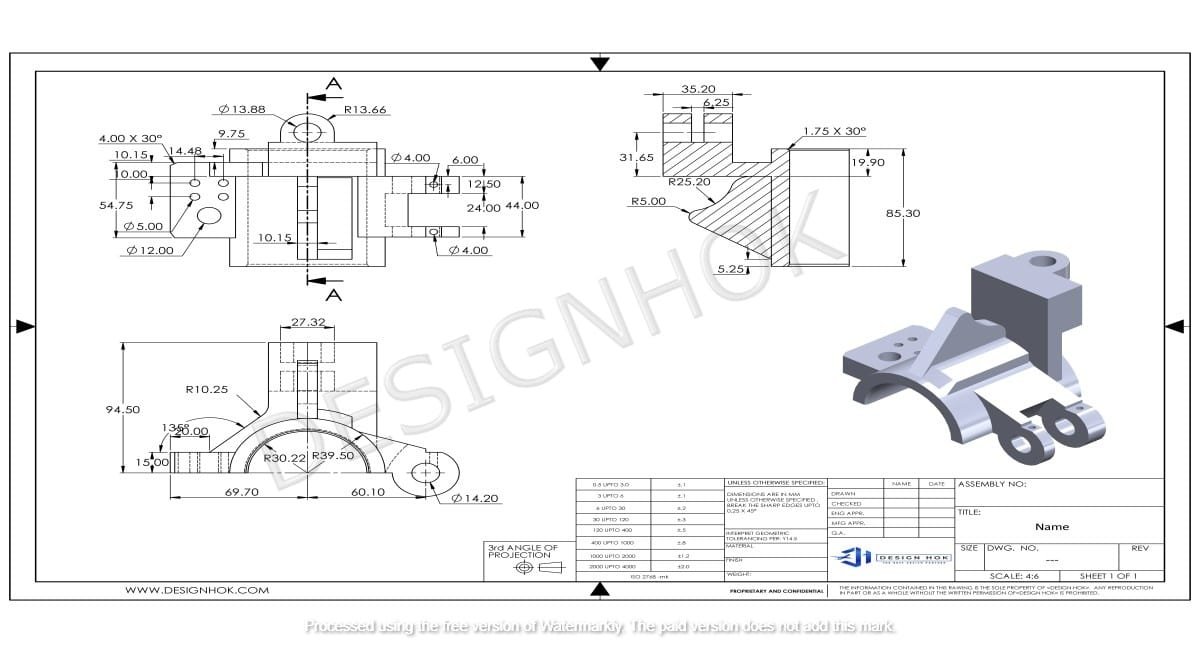
Introduction to Aerospace Mechanical Drawings
Aerospace mechanical drawings are highly detailed technical documents that represent the accurate dimensions of the parts which is needed to build parts used in aircraft, spacecrafts, and different mechanical systems. This mechanical drawing serves as the blueprint. It guides engineers and mechanics, how to manufacture and every step of production. Unlike other drawings, mechanical drawings are extremely different; they have to be so precise because even a minor errors cause major problems.
1. What is The AS 9100 Standard?
AS 9100 is an international quality management standard, developed by the International Aerospace Quality Group (IAQG). It is specially designed for the aerospace industry. It is based on ISO 9001. ISO 9100 is a general quality standard, but it includes some extra requirements(related to safety and reliability), which is why it is called AS 9100. You should visit the Design HOK Services. To manufacture or supply any parts in this industry, they must have to follow these standards. The organisation must show its design and documentation. AS 9100 sets a strict guideline for aerospace companies.
2. Why AS 9100 Matters for Engineering Drawings?
A small error in a mechanical drawing can cause a major failure in an aircraft. This is why every aerospace company has to follow international standards. AS9100 ensures every detail in the drawing follows strict quality standards.
That means
Documented Drawing Revisions: Every drawing revision is meticulously documented and requires approval through a specialized control process.
Supplier Access: Suppliers are granted access exclusively to the most current and updated drawings.
Traceability of Materials: All materials and specifications can be traced back to verified, international sources, ensuring reliability.
Quality Assurance: Consistent part quality is maintained through clearly defined inspection and quality assurance protocols. In easy words, AS9100 is the backbone of an aerospace mechanical drawings company. It ensures the quality and safety of aircraft, which reduces the risk of production errors or in-flight failures.
3. Essential AS 9100 Guidelines for Aerospace Mechanical Drawings
AS9100 follows specific standards strictly; that’s why documentation is important to explain how the drawings are created and how parts are going to be assembled perfectly.
The AS 9100 follows these clauses:
- Clause 1: Scope
- Clause 2: Normative References
- Clause 3: Terms and Definitions
- Clause 4: Context of the Organisation
- Clause 5: Leadership
- Clause 6: Planning
- Clause 7: Support
- Clause 8: Operation
- Clause 9: Performance Evaluation
- Clause 10: Improvement
4. Best Practices for Drawing Creation and Control
When aerospace mechanical drawings companies want to follow the guidelines of AS 9100, it’s not just about the documentation. It’s about building the structure in technical drawing. Each drawing serves as the blueprint for the production process, so it must be precise and reliable. We also use GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing) for precision. In easy words, it can be defined as how flat a surface should be while the assembling.
5. Mistakes to Avoid in Aerospace Mechanical Drawings Drafting
Humans can make errors that jeopardise AS 9100 compliance. Sometimes they forget to update the drawing after a revision, using outdated symbols and non-standard annotation, and lack formal approval signatures on drawings, and inadequately archive legacy drawings.
6. Drawing Management Systems for AS 9100 Compliance
These systems directly support AS 9100’s emphasis on document control and traceability.
We need a proper system to manage our technical drawings. Design HOK software like Product Data Management (PDM) or PLM software that can help designers manage their drawings properly. These tools secure your document access, and you have the right to give role-based editing rights, tracking of revisions, and compliance reporting.
7. Steps to Audit and Maintain Drawing Integrity
Review of drawing regularly: We have to do an inspection daily or once a week to identify incorrect information.
Use Drawing Checklists: Make sure that each file follows all required AS 9100 fields.
Record of Previous Revisions: Maintain historical records for traceability.
Trained Team: Engineers and drafters must understand AS 9100 requirements.
Conduct Internal QMS Audits: Include drawing processes in quality assessments.
These steps are a major key factor in maintaining your certification of AS 9100.
Conclusion
Aerospace drawing is not just a blueprint; these mechanical drawings follow strict international standards to maintain safety. The AS9100 shows its importance by maintaining safety and accuracy consistently.
By following the strict guidelines of AS9100 with your aerospace mechanical drawings, you don’t just follow regulations, but you also build credibility, safety, and global competition in the industry of aerospace mechanical drawings industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What are Aerospace Mechanical Drawings?
Aerospace mechanical drawings are the details representation of 2d and 3D mechanical drawings. It represents parts, including the required specification, tolerance, and material required for production
Q2: How does AS 9100 apply to mechanical drawings?
All mechanical drawing has to be controlled and validated under the AS 9100 requirements. It ensures the team management, revision control, and risk identification related to design documentation.
Q3: What CAD software is best for AS 9100-compliant drawings?
CAD platforms such as CATIA, Siemens NX, SolidWorks, and AutoCAD are widely used. For compliance, they should integrate with PLM systems for traceability and document control.
Q4: Can I use hand-drawn sketches in AS 9100 environments?
We can use hand-drawn sketches, but it is only acceptable in early concepts. For the final manufacturing design, we have to use a tool for perfection.
Q5: Who is responsible for AS 9100 drawing compliance?
The engineer who creates drawings, the drafters, the quality manager, and the lead of design share responsibility for all drawings, and they have to ensure that they follow all the requirements of AS9100.