Exploring 2D Drafting in Machine Design, its applications, benefits, and how Design Hok utilizes this essential tool to bring precise and efficient mechanical designs to life.
Introduction:
The Role of Exploring 2D Drafting in Machine Design
Exploring 2D Drafting in Machine Design has long been a foundational tool in machine design, serving as the blueprint for engineers and designers to transform ideas into tangible products. Even in today’s world of advanced 3D modeling and simulations, Exploring 2D Drafting in Machine Design remains a critical aspect of the design process. For companies like Design Hok, 2D drafting offers a straightforward, precise method for laying out the specifications, dimensions, and details necessary for machine design. 2D drafting is, its significance in machine design, and how Design Hok employs it to enhance design accuracy and efficiency.
What is Exploring 2D Drafting in Machine Design?
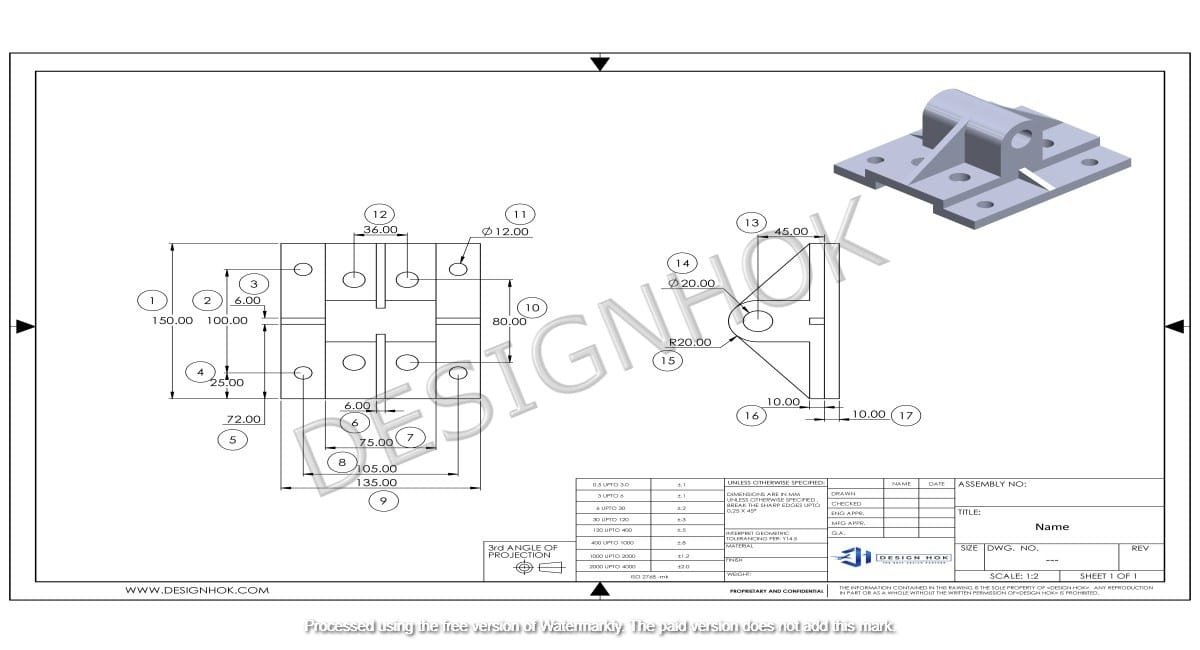
2D drafting refers to the creation of flat, two-dimensional representations of objects. In machine design, 2D drafts are used to produce detailed drawings of machine components, assemblies, and systems. These drawings provide crucial information such as dimensions, tolerances, materials, and manufacturing details. Unlike 3D modeling, which represents objects in three dimensions, 2D drafting focuses on the object’s views—typically the top, front, and side projections—to convey all necessary details for manufacturing and assembly.

Importance of Exploring 2D Drafting in Machine Design
Even though 3D modeling has become increasingly popular, 2D drafting holds a vital place in machine design for several reasons:
- Clarity and Simplicity:
- 2D drafts provide a clear and straightforward view of each component. They break down complex machines into individual parts and assemblies, making it easier to understand how each piece fits and functions within the overall system.
- Detailed Specifications:
- A 2D drawing contains precise measurements, tolerances, and other technical details essential for manufacturing. These specifications ensure that each part is produced accurately and fits perfectly within the assembly.
- Standardization:
- 2D drafting follows established industry standards such as ISO, ANSI, and DIN, which helps maintain consistency and uniformity across different projects. This standardization ensures that manufacturers and engineers worldwide can interpret the designs correctly.
- Cost-Effectiveness:
- Exploring 2D Drafting in Machine Design is often more cost-effective than 3D modeling for simpler components or when only basic information is required. It allows designers to quickly generate drawings without the time and resources needed for full 3D models.
- Manufacturing and Assembly Guidance:
- Exploring 2D Drafting in Machine Design serve as essential guides for machinists and assembly line workers. They provide step-by-step instructions for fabricating and assembling components, reducing errors and improving efficiency in the production process.

Applications of Exploring 2D Drafting in Machine Design
2D drafting is used across various stages of machine design, from the initial concept to the final manufacturing process. Here are some common applications:
- Component Design:
- 2D drafting is used to create detailed drawings of individual machine parts. These drawings include dimensions, material specifications, and tolerances, ensuring that each component is manufactured to precise standards.
- Assembly Drawings:
- In addition to individual components, Exploring 2D Drafting in Machine Design is used to create assembly drawings that show how different parts fit together. These drawings provide a visual guide for assembling the machine, highlighting the order and orientation of components.
- Schematics and Layouts:
- For systems that involve fluid, electrical, or pneumatic components, 2D drafting is used to create schematics and layout diagrams. These drafts help in planning and installing the system’s piping, wiring, and other elements.
- Manufacturing Instructions:
- 2D drafts include notes and instructions for manufacturing processes such as machining, welding, and finishing. These details guide machinists on how to produce and finish each component accurately.
How Design Hok Utilizes 2D Drafting
Design Hok leverages the power of 2D drafting to create precise and functional machine designs. Here’s how they integrate 2D drafting into their design workflow:
- Initial Design Phase:
- In the early stages, Design Hok uses 2D drafting to create basic layouts and concepts. This helps in visualizing the overall design, determining the best approach for component placement, and ensuring that all parts will work together seamlessly.
- Detailed Engineering Drawings:
- Once the initial concept is established, Design Hok produces detailed 2D drafts for each component. These drafts include exact measurements, tolerances, and other specifications necessary for manufacturing, ensuring a high level of accuracy.
- Assembly and System Layouts:
- Design Hok uses 2D drafting to create comprehensive assembly drawings. These drafts show how each component is assembled into the final machine, providing clear instructions for assembly line workers and technicians.
- Collaboration and Communication:
- Exploring 2D Drafting in Machine Design serves as a common language between designers, engineers, and manufacturers. Design Hok uses these drafts to communicate design intent, clarify specifications, and ensure everyone involved in the project has a precise understanding of the design.
Benefits of Exploring 2D Drafting in Machine Design
By incorporating 2D drafting into their design process, Design Hok benefits in several ways:
- Accuracy and Precision:
- 2D drafting ensures that all components are designed to exact specifications, reducing the risk of errors during manufacturing and assembly.
- Efficient Design Process:
- 2D drafts provide a quick and effective way to create, modify, and refine designs, speeding up the overall design process.
- Cost Savings:
- By using 2D drafting for simpler designs or initial layouts, Design Hok can save time and resources compared to more complex 3D modeling when it’s not necessary.
- Enhanced Communication:
- Clear and detailed 2D drafts facilitate better communication between design teams, manufacturers, and clients, leading to smoother project execution.
Conclusion:
The Lasting Value of Exploring 2D Drafting in Machine Design
Exploring 2D Drafting in Machine Design remains a crucial element in machine design, offering clarity, precision, and cost-effectiveness that make it indispensable. For Design Hok, 2D drafting serves as the backbone of the design process, providing the detailed blueprints needed to bring complex mechanical systems to life. While 3D modeling and simulations have their place in modern design, 2D drafting continues to play a vital role in ensuring that machine designs are accurate, functional, and ready for production.
FAQs
1. What is 2D drafting in machine design?
2D drafting is the process of creating two-dimensional drawings that represent the detailed specifications of machine components and assemblies. It includes information such as dimensions, tolerances, and material specifications.
2. Why is 2D drafting important for machine design?
2D drafting is important because it provides clear, detailed instructions for manufacturing and assembling machine components. It ensures accuracy, standardization, and effective communication among engineers, designers, and manufacturers.
3. How does 2D drafting differ from 3D modeling?
While 3D modeling provides a three-dimensional representation of an object, 2D drafting focuses on flat, two-dimensional views, such as top, front, and side projections. 2D drafting is typically used for creating detailed technical drawings needed for manufacturing.
4. Can 2D drafting be used alongside 3D modeling?
Yes, 2D drafting is often used alongside 3D modeling. While 3D models help visualize and simulate the design, 2D drafts provide the detailed specifications and instructions needed for manufacturing and assembly.
5. What software is commonly used for 2D drafting?
Common software for 2D drafting includes AutoCAD, DraftSight, and SolidWorks. These tools allow designers to create precise technical drawings with detailed specifications.
6. What are the key components of a 2D draft?
A 2D draft typically includes views of the component (top, front, side), dimensions, tolerances, material specifications, and notes on manufacturing processes.
7. How does 2D drafting improve the manufacturing process?
2D drafting provides clear and precise instructions for manufacturing, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring that each component is produced to the correct specifications. This leads to more efficient and accurate production.
8. Why does Design Hok use 2D drafting in its machine design process?
Design Hok uses 2D drafting to create accurate and detailed blueprints for their machine designs. It helps them ensure precision, communicate effectively with manufacturers, and streamline the design-to-production process.
9. Is 2D drafting still relevant with the rise of 3D modeling?
Yes, 2D drafting remains relevant as it provides detailed technical drawings that are essential for manufacturing. While 3D models offer visualization and simulation, 2D drafts are crucial for specifying exact dimensions and assembly instructions.
10. What industries commonly use 2D drafting for machine design?
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, construction, and industrial machinery commonly use 2D drafting for creating precise mechanical designs and assembly instructions.