What Does a Mechanical Engineer Do? A Complete Guide
Mechanical engineering is one of the oldest and most important branches of engineering. It has always been the foundation of industrial growth and modern inventions. But here’s what you may think: what does a mechanical engineer really do? They didn’t just design and manufacture machines. They use algebra, creativity, and technology to design and build systems that make life easier. They are the problem-solvers who design, test, and improve the machine and tools that keeps the world running. In this guide, we’ll learn what does a mechanical engineer do? every day, what skills they need, and what the future of mechanical engineering holds.
Daily Work of a Mechanical Engineer
The job of a mechanical engineer is more than creating machines. Their work is analytical and highly collaborative.
Concept Design and Product Development
Engineers study the client’s needs or market demand and then generate new ideas and bring them into the real world by using CAD software. They run early tests and simulations to make sure the idea is possible and efficient. For example, if the goal is to design a new engine, the engineer will study everything about engine’s such as power output, weight, temperature limits, and fuel. Design HOK makes it affordable and easy to manufacture.
Material Selection and Stress Analysis
Choosing the right material is a big part of the job. Every machine or part must be strong enough to save energy, then they evaluate metal, composite, or polymers based on the required strength, weight, and cost. They also run a stress analysis and tests using a computer to make sure the product won’t break or deform under pressure.
Prototype Development
Once the design is ready, it’s time to build a beta version of the real product. The question is, what does a Mechanical engineer do? Supervise this step very closely. Then they perform tests to check if the prototype works as planned or not. If anything happens, then they go back and fix it. This process may repeat several times until the product meets all performance and safety standards. These tests include measuring vibration, checking strength, and temperature limit. It evaluates the fuel cost and how much energy it consumes.
Manufacturing and Production Support
When everything is working accurately and there’s no such failure during beta testing, then it moves into mass production. Engineers collaborate with manufacturers to make sure that the product is made exactly as designed. They might also design tools to make production smoother. For example, when building an aeroplane engine, a mechanical engineer ensures that each part fits perfectly and meets international standards.
Maintenance and System Improvement
Engineers also handle maintenance and performance upgrades for machines already in use — like factory systems, power plants, or vehicles. What does a Mechanical engineers do? also ensure that the system continues running smoothly. They analyse performance data and suggest improvements to increase efficiency. For example, they modify a turbine to generate more power or change materials to make it last longer.
Industries That Rely on Mechanical Engineers
Mechanical engineers play an essential role across many industries.
- Aerospace
- Automotive.
- Energy
- Healthcare
- Manufacturing
Now, no matter what your field is, What does a mechanical engineer do? use analytical thinking and technical expertise to create solutions that improve the quality of life.
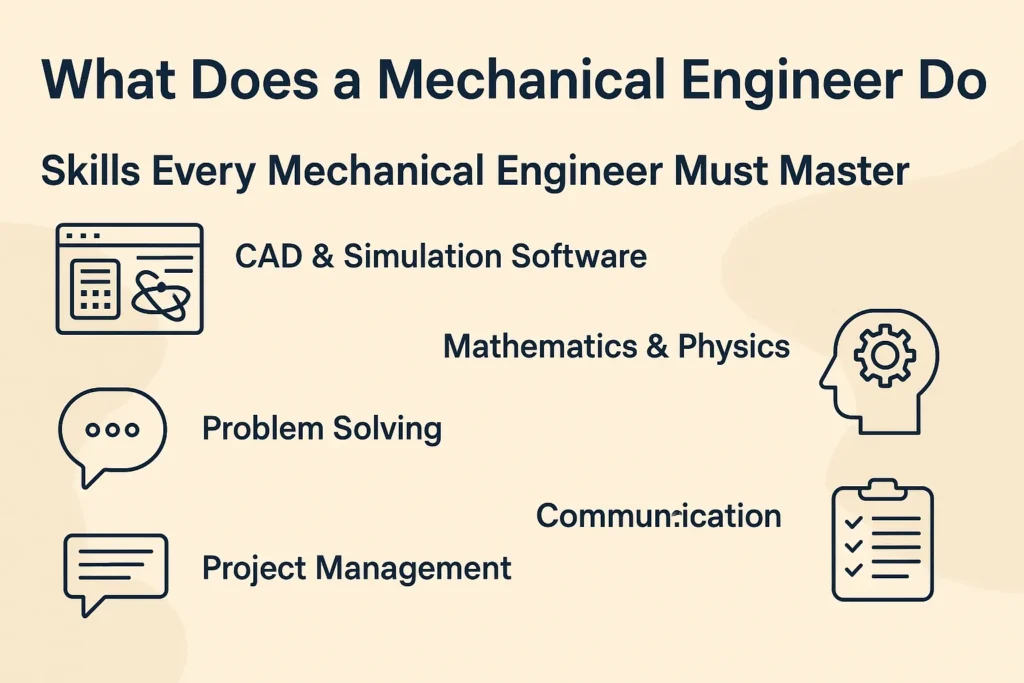
Skills Every Mechanical Engineer Needs
In this field, you have to be an expert in technical knowledge and practical skills if you want to be successful. In technical skills, you need a knowledge of CAD and simulation software like SolidWorks or AutoCAD, and you also need some basic understanding of physics, data analysis, and manufacturing methods. You also need some soft skills in this field, such as problem-solving, teamwork, and time management..
Career Growth and Pathways
To enter this field, you have to do a bachelor’s degree in mechanical engineering. During studies, students learn about physics, mechanics, and manufacturing. Some engineer also continue their education with a master’s degree or specialise in areas such as robotics or design engineering. As the experience grows by the period of time, they can move into research and development, project management, or may become technical directors.
Real-World Applications of Mechanical Engineers
In short, what does a mechanical engineer do? They are behind everything that can move. Here are a few examples given below of how they improve the world.
- They design vehicles in the automotive industry and make your vehicle comfortable and safer.
- They create an energy system that uses wind or solar power.
- They build different machines for medical services that help surgeons perform surgery.
- They develop a machine that filters the water for remote areas.
Their work isn’t just to build machines, but they also solve human problems and make life better for everyone.
Challenges in Mechanical Engineering
You must face challenges at almost every stage of life. So, like any career, mechanical engineering also faces real challenges.
- In this field, engineers have to meet strict deadlines, budgets, and safety standards.
- Some machine takes too much time for testing, or sometimes you have to work extra hours to meet the production deadline.
- In this field, you must keep updating your skills.
- Even a small mistake by an engineer can cause a safety risk or lead to product failure.
Engineers still love this job; they love to solve complex problems.
The Future of Mechanical Engineering
The future of What does a mechanical engineer do? It is bright because the modern world is entering an era of automation and artificial intelligence.
Here are the modern fields for upcoming engineers.
- An automated machine that uses artificial intelligence to predict and fix problems automatically.
- Robots that perform surgery or assist in dangerous environments.
- Electric and hydrogen-powered vehicles that reduce pollution.
- Smart manufacturing systems that use sensors and data to improve production.
- Green energy projects such as wind turbines, solar systems, and biofuels.
- Space exploration technologies for Mars missions and satellite systems.
Expert Insight
In this modern world, mechanical engineers are evolving into “ Digital engineers”. They must know the process of manufacturing and how to write code, and those who know about AI and cloud-based design tools will have the edge in the job market.
The future of these engineers will be:
- Creative and adaptable to global challenges like climate change
- Advance understanding in digital tools and AI.
- Highly skilled in CAD, robotics, and manufacturing.
Final Thoughts
You may think What do mechanical engineers do? They are thinkers and creators of technology that empower the modern world. Mechanical engineers improve the safety of our lives by making vehicles safer, smarter machines, and cleaner energy. Engineers use science to turn imagination into working solutions by blending their creativity and logic.






Nice post. I learn something more challenging on different blogs everyday. It will always be stimulating to read content from other writers and practice a little something from their store. I’d prefer to use some with the content on my blog whether you don’t mind. Natually I’ll give you a link on your web blog. Thanks for sharing.
Hi! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok. I’m undoubtedly enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.