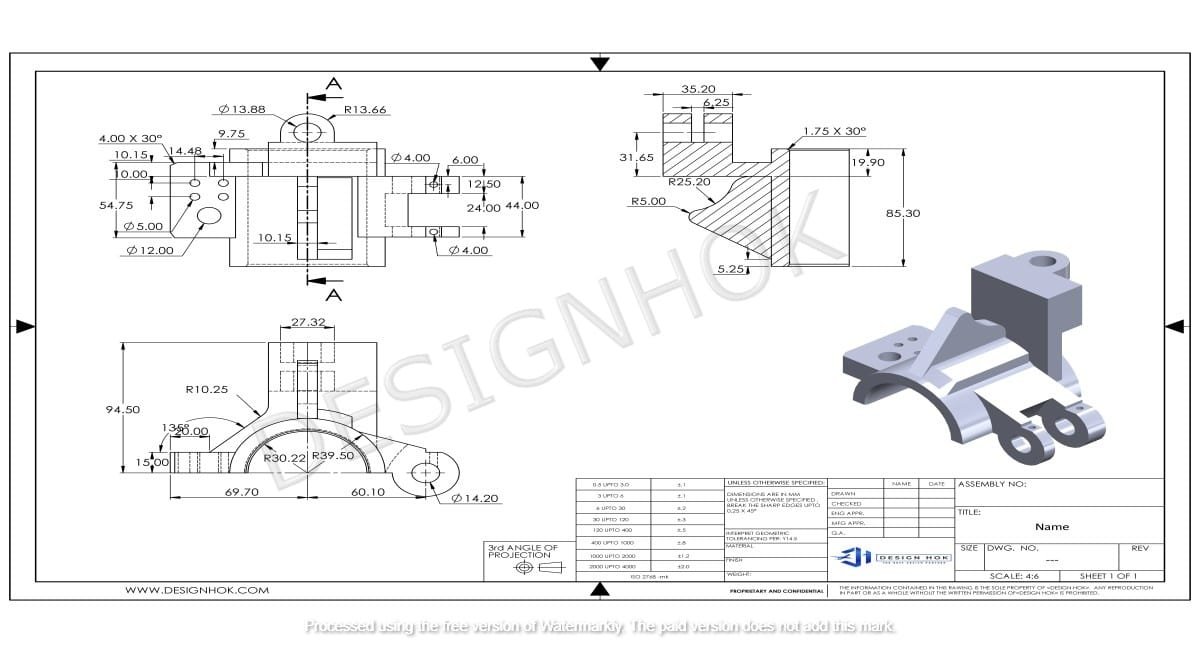
Description:
The world of design and engineering relies heavily on drawings to communicate ideas and bring projects to life. While both 2D and 3D drawings serve as essential tools, they differ significantly in terms of representation, complexity, and application. This article explores the key differences between 2D and 3D drawings, helping you understand when and why each type is used in various industries.
What are Differences Between 2D and 3D Drawings?
2D drawings, or two-dimensional drawings, are flat representations that consist of height and width but lack depth. These drawings are typically created using traditional methods like paper sketches or computer-aided design (CAD) software. Commonly used in architectural blueprints, mechanical schematics, and electrical plans, 2D drawings provide essential information about the dimensions and layout of an object or structure.
Differences Between 2D and 3D Drawings often use standardized symbols, lines, and measurements to communicate specific details about an object’s geometry. In the manufacturing industry, for example, Differences Between 2D and 3D Drawings might include detailed views such as front, side, and top projections, enabling engineers and machinists to visualize how components will be constructed. These types of drawings are typically easier and quicker to produce, making them cost-effective for projects that don’t require a high level of detail.
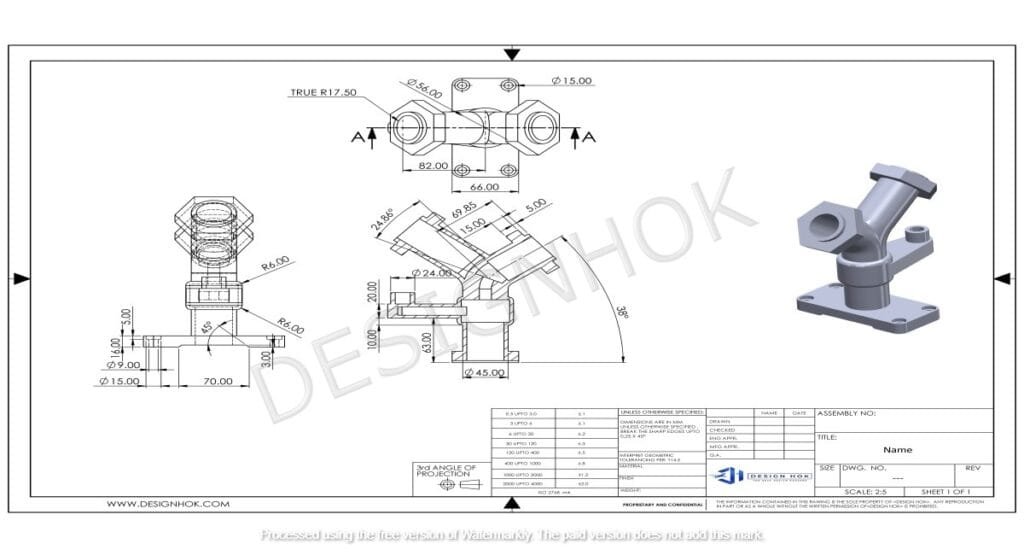
What are Differences Between 2D and 3D Drawings?
On the other hand, Differences Between 2D and 3D Drawings, or three-dimensional drawings, incorporate depth in addition to height and width. These drawings give a more realistic representation of objects, structures, or spaces by simulating how they appear in real life. 3D drawings are typically created using advanced CAD software that allows designers to visualize an object from every angle.
In fields such as architecture, product design, and engineering, 3D drawings are widely used to provide more comprehensive insights into the design. For example, in construction projects, 3D models can be used to show not just the exterior structure of a building but also the interior layout, plumbing, and electrical systems. They allow stakeholders to better understand spatial relationships, materials, and other critical factors before the project enters the construction phase.
Key Differences Between 2D and 3D Drawings
1. Dimensions:
The most obvious Differences Between 2D and 3D Drawings is the number of dimensions they represent. 2D drawings only convey height and width, offering a flat perspective. In contrast, 3D drawings represent height, width, and depth, giving a more complete view of the object or structure.
2. Detail and Realism:
Differences Between 2D and 3D Drawings are often more abstract and symbolic, relying on standardized symbols and views to convey information. 3D drawings, however, are much more realistic, showing how an object would look and function in real life. This makes 3D drawings especially useful for visualizing complex designs where the interaction of different parts is critical.
3. Ease of Creation:
Differences Between 2D and 3D Drawings are typically simpler and faster to create, especially for small-scale projects. Traditional sketches or CAD software can generate 2D plans quickly without the need for complex modeling. On the other hand, creating 3D drawings requires more advanced software, time, and expertise, as it involves rendering multiple angles, textures, and materials.
4. Cost:
Due to their simplicity, Differences Between 2D and 3D Drawings are generally less expensive to produce. They require fewer resources and less time compared to 3D drawings, which often involve higher costs due to the need for specialized software and skilled labor.
5. Applications:
Differences Between 2D and 3D Drawings are ideal for projects that require clear, straightforward communication of design concepts, such as construction blueprints, floor plans, or mechanical drawings. 3D drawings, on the other hand, are preferred in industries like animation, video game design, virtual reality, and architectural visualization, where a detailed and immersive representation is crucial.
6. Interactivity and Flexibility:
With 3D drawings, users can interact with the model by zooming in, rotating it, or exploring it from different angles. This level of interactivity is impossible with 2D drawings, which are static and provide limited perspectives.
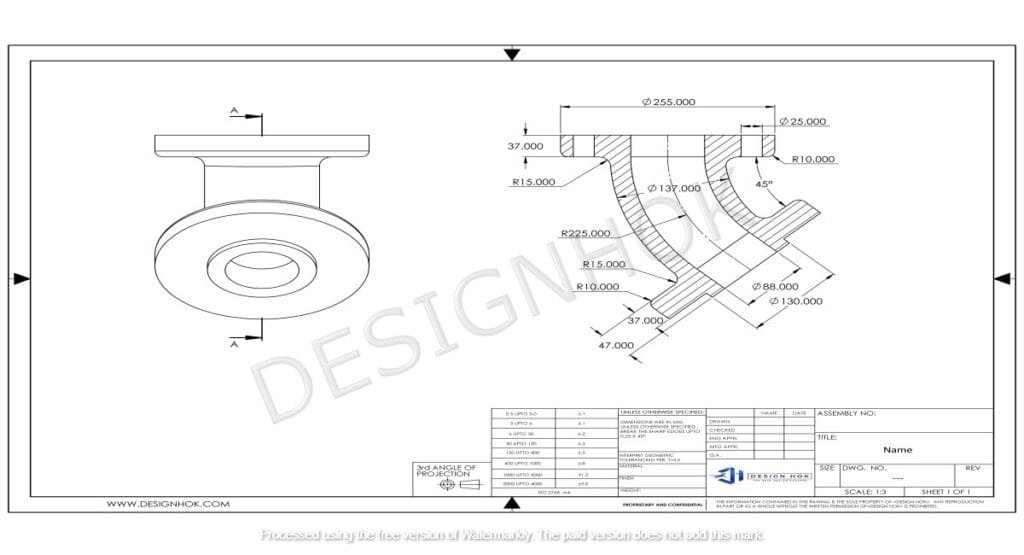
Which One Should You Use?
The decision to use Differences Between 2D and 3D Drawingss largely depends on the project’s requirements. For simpler designs or projects with tight budgets, 2D drawings may suffice. They are effective at conveying essential information in a cost-efficient manner. However, if the project demands greater detail, complexity, or visualization from multiple perspectives, 3D drawings are the better choice.
For example, in manufacturing, where precision is critical, 3D models can help identify potential design flaws that might not be visible in 2D drawings. Similarly, in architecture, 3D drawings allow clients to take virtual walkthroughs of a building, providing a more immersive experience that 2D drawings can’t offer.
Conclusion
Both 2D and 3D drawings serve important roles in the world of design and engineering. While 2D drawings are simpler, faster, and more cost-effective, 3D drawings provide a more realistic, detailed, and interactive representation of the project. Understanding the differences between these two types of drawings helps you choose the right one based on your project’s goals, complexity, and budget. In many cases, designers use a combination of both to ensure they meet all technical and visual requirements.
FAQs
1. Can 2D drawings be converted into 3D drawings?
Yes, with the right software, 2D drawings can often be converted into 3D models. This process, however, may require manual adjustments to ensure accuracy.
2. Are 3D drawings always better than 2D drawings?
Not necessarily. The choice depends on the project. For simple designs and projects with tight budgets, 2D drawings can be more efficient and cost-effective.
3. What industries rely on 3D drawings the most?
Industries such as architecture, product design, film and animation, and video game development heavily rely on 3D drawings to create detailed and immersive designs.
4. Can I use both 2D and 3D drawings in a single project?
Yes, many projects use both types of drawings. 2D drawings are often used for detailed technical information, while 3D drawings provide a visual overview of the final design.