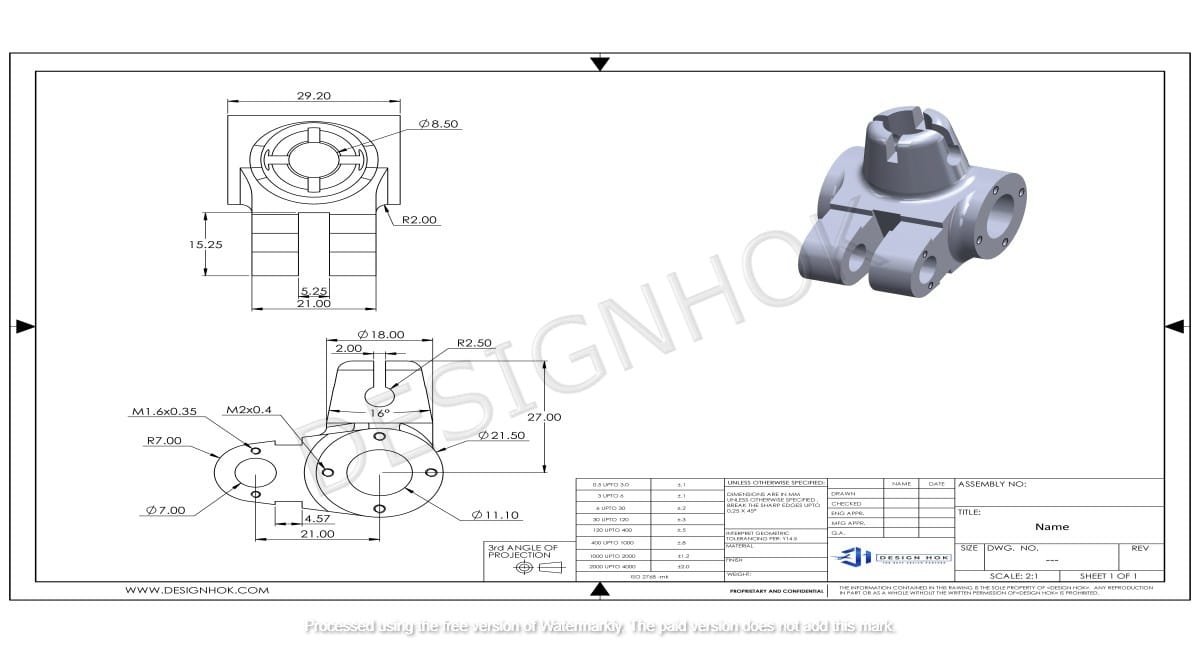
Introduction:
Why Choose 3D Modeling with Blender?
Blender is an open-source, powerful, and versatile tool widely used in various industries for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. For Design Hok, Blender offers a cost-effective solution that rivals expensive commercial software, making it an excellent choice for professionals and hobbyists alike. This blog will guide you through the process of using 3D Modeling with Blender for Design Hok, highlighting key features and providing tips for effective design creation.
Getting Started with Blender
Before diving into the intricacies of 3D Modeling with Blender, it’s essential to set up Blender correctly and familiarize yourself with its interface and tools.
1. Downloading and Installing Blender
Blender is free to download and use, available for Windows, macOS, and Linux. To get started:
- Download the latest stable version for your operating system.
- Install the software by following the on-screen instructions.
2. Understanding 3D Modeling with Blender Interface
Blender’s interface may seem daunting at first, but it becomes intuitive with practice. Key areas include:
- 3D Viewport: The primary workspace where you create and manipulate 3D models.
- Outliner: A hierarchical view of all objects in your scene, allowing you to organize and manage them efficiently.
- Properties Panel: Offers detailed settings for objects, materials, rendering, and more.
- Toolbar: Contains tools for transforming objects, adding new elements, and modifying existing ones.
Spend some time exploring the interface to understand where everything is located.
Creating Your First 3D Modeling with Blender
Once you’re comfortable with the interface, it’s time to create your first 3D model. For this tutorial, we’ll design a simple product concept that could be used in a Design Hok project.
1. Starting a New Project
- Open 3D Modeling with Blender and start a new project by selecting “General” from the splash screen.
- You’ll see a default cube in the 3D viewport. This cube can be manipulated or replaced with a different object depending on your design needs.
2. Basic Object Manipulation
Blender offers several tools for manipulating objects:
- Translate (Move): Press
Gto move an object. You can constrain the movement to a specific axis by pressingX,Y, orZafter pressingG. - Rotate: Press
Rto rotate an object. Similar to moving, you can constrain the rotation to a specific axis. - Scale: Press
Sto scale an object. Constrain scaling to a specific axis by pressingX,Y, orZ.
Experiment with these tools to get a feel for how they affect objects in the 3D space.
3. 3D Modeling with Blender with Basic Shapes
3D Modeling with Blender provides a variety of basic shapes (meshes) to start your model:
- To add a new object, press
Shift + Aand select a mesh (e.g., cube, sphere, cylinder). - Use the translate, rotate, and scale tools to position and shape these meshes into your desired form.
For example, if you’re designing a product prototype, start with a cylinder for the base and a cube for the main body. Combine these basic shapes and refine them as needed.
4. Editing the Mesh
To create more complex shapes, you’ll need to enter Edit Mode:
- Select your object and press
Tabto enter Edit Mode. - In Edit Mode, you can manipulate vertices, edges, and faces of your mesh. This allows you to create intricate details and customize the shape.
Key tools in Edit Mode include:
- Extrude (E): Extends a face or edge outward, adding new geometry to your model.
- Loop Cut (Ctrl + R): Adds a new loop of vertices around your mesh, allowing for more detailed modeling.
- Knife Tool (K): Allows you to cut new edges into your mesh for additional customization.
Use these tools to refine your model, adding the necessary details to match your design vision.
Optimizing Your Model for 3D Modeling with Blender
Creating a 3D Modeling with Blender is just the beginning. To ensure that your design is functional and efficient, follow these optimization steps:
1. Managing Polygon Count
High polygon counts can slow down your project and make it difficult to work with. Optimize your model by reducing unnecessary geometry:
- Decimate Modifier: Apply the Decimate Modifier in the Properties Panel to reduce the polygon count while preserving the model’s shape.
- Manual Reduction: In Edit Mode, manually remove unnecessary vertices, edges, and faces.
2. Applying Materials and Textures
Materials and textures give your model a realistic appearance:
- Materials: Go to the Materials tab in the Properties Panel. Click “New” to create a new material and adjust its properties (e.g., color, roughness).
- Textures: Add textures to your material by selecting the texture tab and loading an image file. Blender offers procedural textures as well, which can be adjusted for various effects.
For Design Hok, realistic materials help clients visualize how the final product will look.
3. Using Modifiers for Advanced 3D Modeling with Blender
Modifiers are non-destructive tools that can change the appearance of your model:
- Subdivision Surface: Smoothens your model by adding more geometry. Great for creating organic shapes.
- Boolean: Combines or subtracts one shape from another. Useful for cutting holes or combining multiple objects into one.
Rendering and Exporting Your Model
Once your model is complete, it’s time to render and export it for presentation or further use.
1. Setting Up the Scene
- Lighting: Add light sources to your scene by pressing
Shift + Aand selecting a light type (e.g., Point, Sun). Adjust their intensity and position to highlight your model. - Camera: Position the camera by pressing
Shift + Aand adding a camera object. Adjust its angle to get the best view of your model.
2. Rendering the Model
- Go to the Render tab in the Properties Panel.
- Choose your render engine (Eevee for quick previews, Cycles for high-quality renders).
- Adjust the resolution and output settings.
- Press
F12to render the image. Save the rendered image usingImage > Save Asin the render window.
3. Exporting the Model
- To export your model, go to
File > Export. - Choose the file format that suits your needs (e.g., .FBX, .OBJ, .STL).
- Adjust export settings as necessary and click “Export.”
Your model is now ready for use in other software, presentations, or as a prototype for Design Hok.
Conclusion:
3D Modeling with Blender
3D Modeling with Blender is a powerful tool that, when mastered, can greatly enhance the 3D modeling process in Design Hok projects. Its flexibility, combined with the ability to create detailed and precise models, makes it a valuable asset for designers. By following this guide, you can begin to harness Blender’s capabilities to bring your ideas to life, creating models that are not only visually impressive but also optimized for real-world applications.
FAQs
1. Is Blender suitable for professional design projects at Design Hok?
Yes, Blender is a professional-grade tool that offers robust features suitable for design projects across various industries. Its open-source nature also makes it highly customizable.
2. Can Blender handle complex models with high detail?
Absolutely. Blender is capable of handling highly detailed models, especially with its powerful tools like the Subdivision Surface Modifier and sculpting features.
3. How can I improve the performance of Blender when working with large models?
You can improve performance by optimizing your model’s polygon count, using layers to manage visibility, and adjusting Blender’s viewport display settings to reduce load.
4. What file formats can Blender export for use in other software?
3D Modeling with Blender supports a wide range of file formats, including .FBX, .OBJ, .STL, .DAE, and .PLY, making it compatible with most other 3D modeling and CAD software.
5. Is Blender difficult to learn for beginners?
Blender has a steep learning curve, but with practice and resources like tutorials, users can quickly become proficient. Its community is also very supportive, offering a wealth of knowledge and tools.
6. Can I use Blender for tasks other than 3D modeling?
Yes, Blender is also used for animation, video editing, sculpting, and even game design. It’s a versatile tool that can handle various aspects of the design process.
7. Does Blender support collaborative work?
While Blender is primarily a single-user tool, it supports collaborative workflows through file sharing, version control systems, and third-party add-ons that enable team collaboration.
8. How often is Blender updated?
Blender is actively developed, with frequent updates that introduce new features, improvements, and bug fixes. Users can stay updated with the latest versions to benefit from these enhancements.