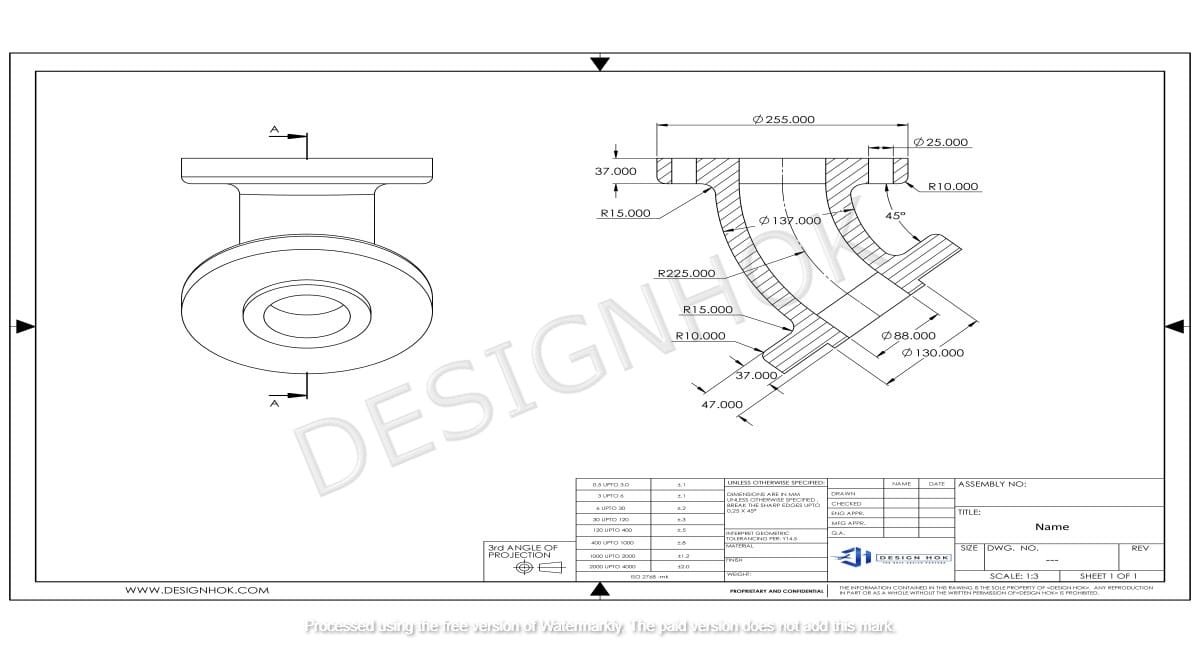
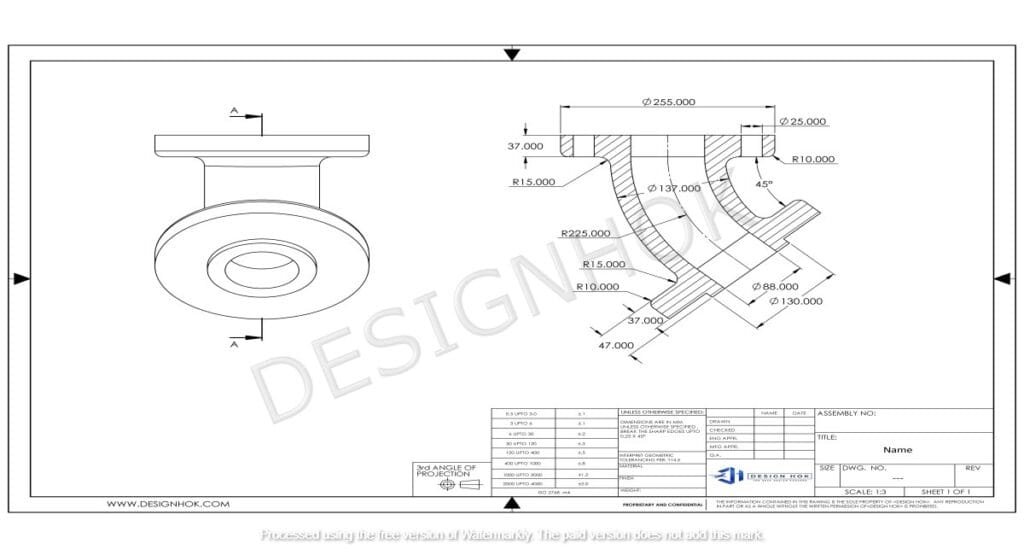
Description:
2D Drawing in Engineering remain an integral tool for engineers, providing essential insights for the conceptualization, design, and implementation of projects. Despite advancements in 3D modeling, 2D drawings offer precision and clarity for specific applications, such as component layout, manufacturing, and technical documentation. This article explores the critical applications of 2D drawings in engineering, examining their impact on design accuracy, project planning, and effective communication among multidisciplinary teams.
Understanding the Role of 2D Drawings in Engineering
In engineering, 2D Drawing in Engineering offer a simplified view that allows engineers to represent complex systems, products, or parts in manageable detail. These drawings help in visualizing structures, systems, and components, allowing engineers to present technical details clearly and unambiguously. Although 3D modeling has brought significant advancements, 2D drawings are still widely used because they provide essential design data in a straightforward, accessible manner.
Key Applications of 2D Drawing in Engineering
1. Component and Assembly Layouts
- Precision in Part Dimensions: 2D Drawing in Engineering allow engineers to specify precise dimensions, tolerances, and alignments, critical for creating individual parts that fit seamlessly in larger assemblies.
- Efficient Assembly Views: These drawings enable engineers to visualize each component’s position and orientation within an assembly, ensuring they understand how parts should fit together before manufacturing.
- Simplified Change Management: Engineers can revise designs by adjusting layouts, simplifying the process of refining and improving designs without remaking entire 3D models.
2. Manufacturing and Production Guidance
- Blueprints for Manufacturing: 2D Drawing in Engineering act as blueprints, providing manufacturers with necessary details about the materials, dimensions, and processes required to produce components or products.
- Conveying Technical Specifications: Critical details like surface finish, machining processes, and material specifications are communicated effectively, helping to ensure that manufacturing adheres to design standards.
- Streamlining Quality Assurance: 2D drawings provide a point of reference for quality control, helping inspectors verify that manufactured parts meet specified tolerances and measurements.
3. Schematics for Electrical and Plumbing Systems
- Circuit Diagrams: In electrical engineering, 2D schematics are essential for circuit designs, showing connections between components, wire layouts, and other critical details for construction or troubleshooting.
- Plumbing and Piping Layouts: Engineers use 2D layouts to map out fluid systems like plumbing or HVAC piping, specifying pipe types, lengths, and connections in a manageable visual format.
- Signal and Power Distribution: In complex systems, 2D schematics help engineers organize signal paths and power sources, supporting clarity in the design and maintenance stages.
4. Civil Engineering and Site Planning
- Site Plans: In civil engineering, 2D Drawing in Engineering are crucial for creating site layouts, including roads, utilities, and landscape elements, which help ensure accurate project execution.
- Topographical Mapping: Civil engineers often use 2D Drawing in Engineering for topographical maps that provide details on land elevations, drainage, and other features critical for construction planning.
- Infrastructure Layouts: Roads, pipelines, and other infrastructure elements are detailed through 2D drawings to guide construction teams on placement, measurements, and required materials.
5. Technical Documentation and Standards Compliance
- Documentation for Maintenance: 2D Drawing in Engineering serve as essential documentation that helps technicians troubleshoot, maintain, and repair systems or equipment efficiently.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Many industries require 2D documentation to comply with safety and quality standards, which ensures that designs meet regulatory requirements for usability and safety.
- Creating User Manuals and Technical Guides: For end-users and operators, 2D diagrams illustrate instructions or highlight critical components, making manuals more understandable.
6. Project Planning and Workflow Management
- Resource Allocation and Costing: By clearly showing the parts and materials required, 2D Drawing in Engineering help project managers allocate resources effectively, plan budgets, and ensure cost-effective production.
- Timeline and Milestone Planning: Engineers use 2D drawings to illustrate specific project phases, making it easier to coordinate tasks among teams and track progress accurately.
- Facilitating Communication Across Teams: These drawings act as a common reference, allowing team members from different disciplines to collaborate effectively by providing a shared understanding of the project’s requirements.
Conclusion
In the evolving field of engineering, where precision and clarity are paramount, 2D drawings remain a cornerstone of effective project design and implementation. They allow engineers to convey technical details with unmatched simplicity and accessibility, supporting production, documentation, and cross-disciplinary communication. As technology advances, the complementary use of 2D drawings alongside 3D models will continue to optimize engineering workflows, ensuring accuracy, reliability, and efficiency across diverse engineering projects.
FAQs
Q1: Why are 2D drawings still used when 3D modeling is available?
A1: While 3D models offer detailed visualization, 2D drawings are more accessible and provide specific details with clarity and precision. They are easier to interpret, especially in manufacturing and assembly, where concise details are critical.
Q2: How do 2D drawings improve manufacturing quality control?
A2: 2D drawings specify exact dimensions, tolerances, and other design details, which allows quality control teams to verify that parts and components are made precisely according to design specifications.
Q3: What role do 2D drawings play in civil engineering projects?
A3: Civil engineers use 2D drawings for site layouts, topography, infrastructure design, and utility mapping, which are essential for construction planning and accurate project execution.
Q4: How do 2D drawings aid in project documentation?
A4: 2D drawings serve as valuable references for maintenance, compliance, and troubleshooting, providing clear visual documentation that supports technicians, engineers, and operators.
Q5: Can 2D drawings be used with 3D models?
A5: Yes, 2D drawings are often used in conjunction with 3D models to provide additional detail, serve as blueprint references, and simplify information for specific project requirements.