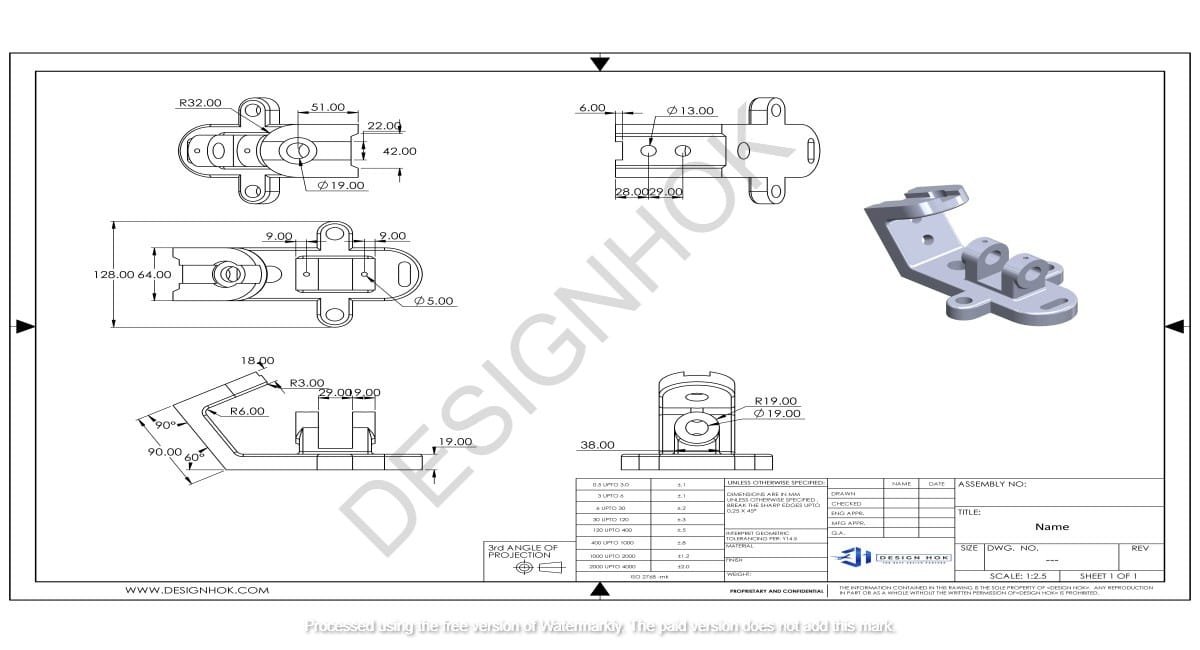
INTRODUCTION:
2D assembly design plays a critical role in manufacturing and engineering, providing clear, precise visuals that outline how individual components come together in an assembly. The importance of 2D assembly design, its applications in various industries, and the essential steps to create effective assembly drawings. 2D design enhances clarity, accuracy, and efficiency in assembly processes
What is 2D Assembly Design?
2D assembly design is the process of creating two-dimensional drawings that show how parts connect and interact to form a larger assembly. These drawings focus on the spatial arrangement, fit, and relationship between different components, providing clear visual guidance for assembly teams and manufacturers. 2D assembly designs emphasize precise measurements, component placement, and fit details, making them essential for efficient and accurate assembly.
Why 2D Assembly Design is Important
The simplicity and clarity of 2D assembly drawings make them ideal for a range of applications:
- Precision and Detail: 2D designs can highlight specific areas of an assembly with exact dimensions and alignments, ensuring accuracy.
- Cost-Efficiency: 2D drawings require fewer resources than 3D models, especially for basic assemblies.
- Ease of Understanding: Assembly teams find it easier to interpret and follow simple 2D layouts without specialized training.
- Time-Saving: Clear, direct 2D drawings speed up assembly, reducing errors and saving time.
Applications of 2D Assembly Design in Industry
2D assembly design is widely used across various sectors, such as:
- Manufacturing: For creating detailed assembly instructions for machinery and equipment.
- Automotive: To illustrate the arrangement of car components like engine parts, chassis, and bodywork.
- Aerospace: For highly accurate layouts in aircraft and spacecraft assembly.
- Electronics: To showcase circuit board layouts and connections in a clear, straightforward way.
Key Components of a 2D Assembly Drawing
To ensure that a 2D assembly design is both informative and practical, it should include:
- Component Views: Standard views (top, front, side) for accurate visualization.
- Dimensions and Measurements: Precise lengths, widths, and distances between components.
- Assembly Instructions: Step-by-step guidance for connecting parts.
- Parts List: A detailed list identifying each component in the assembly.
- Annotations: Additional notes for assembly, such as torque settings or alignment requirements.
Steps to Create an Effective 2D Assembly Design
Creating a successful 2D assembly drawing involves several steps that ensure the final design is both functional and easy to follow.
1. Define the Assembly Structure
Begin by identifying the components and their arrangement within the assembly. The order of assembly matters, so outlining this early helps keep the process efficient.
2. Choose the Right Views
2D drawings typically include top, front, and side views. Select the views that offer the clearest representation of how parts fit together.
3. Accurate Dimensioning
Precision is essential in 2D assembly design. Adding exact dimensions for each part and spacing between them reduces the risk of misalignment and assembly errors.
4. Label Each Component
Each part should be clearly labeled with reference numbers or names. This labeling corresponds to the parts list, which helps assembly teams quickly identify components.
5. Include Clear Assembly Instructions
Detailed instructions make the assembly process straightforward. Specify the order in which parts are connected, and include special instructions where needed, such as bolt torque settings.
6. Add Annotations for Clarity
Annotations clarify certain steps or areas that may require additional attention. These notes may include alignment tips, material types, or handling instructions.
Common Challenges in 2D Assembly Design
Despite its benefits, there are a few challenges associated with 2D assembly design:
- Limited Depth Perception: Since 2D drawings lack the depth and realism of 3D models, complex assemblies might need supplementary images.
- Potential for Misinterpretation: If not drawn with absolute clarity, 2D designs can sometimes lead to misinterpretation.
- Revisions and Updates: Adjustments to 2D assembly designs can be time-consuming, especially if changes affect multiple parts or layers.
Advantages of 2D Assembly Design Over 3D Modeling
While 3D modeling is popular, 2D assembly design offers distinct advantages in certain contexts:
- Simplicity and Accessibility: 2D drawings are universally accessible and can be understood by anyone with basic technical knowledge.
- Lower Cost and Time Investment: Creating 2D drawings generally requires less time and cost than building 3D models, especially for straightforward assemblies.
- Faster Approval Processes: 2D designs can be more easily reviewed and approved by project managers, speeding up the workflow.
Best Practices for 2D Assembly Design
To maximize the effectiveness of a 2D assembly drawing, consider these best practices:
- Standardize Symbols and Notations: Consistency in symbols and notations makes designs easier to interpret.
- Use Clear Line Weights: Differentiating line weights helps highlight important sections and boundaries.
- Optimize for Clarity: Avoid overcrowding the drawing with excessive details; focus on essential information.
- Review and Test: Have the drawing reviewed by others to confirm accuracy and clarity, and consider running a test assembly if possible.
Tools for Creating 2D Assembly Designs
Several software options are available for creating precise 2D assembly designs:
- AutoCAD: Widely used for its accuracy and versatility in creating technical drawings.
- SolidWorks: Known for both 2D and 3D capabilities, making it suitable for assembly design.
- DraftSight: A user-friendly software designed for quick and efficient 2D drafting.
Conclusion
2D assembly design is a foundational tool in engineering and manufacturing. By offering a clear and direct way to visualize component relationships, 2D drawings support faster, more accurate assembly processes and improve communication across teams. When done correctly, these designs streamline production, reduce errors, and ultimately save time and resources. While 3D modeling has its place, the simplicity and precision of 2D assembly drawings ensure they remain a valuable resource in many industries.